Research Article - (2025) Volume 15, Issue 1
Background: COVID-19 pandemic is an unexpected event, which has many effects on people and their lifestyle. Fishermen community possess a unique folk characteristic. Their occupational impact, and health seeking behaviour were not studied much.
Aims and objective: To assess the occupational impact on fishermen community, health seeking behaviour during COVID-19 and their knowledge, attitude, practice of healthy habits in preventing COVID-19 transmission.
Materials and methods: A community based cross-sectional study was conducted among the fishermen community in Puducherry. The sample size was estimated as 216, assuming that 50% of the study population had occupational impact due to COVID-19. Simple random sampling method was employed. The data was collected using a pilot tested semi-structured questionnaire for 2 months and analysed using SPSS 20 version. Frequency distribution along with correlation was employed to test statistical significance.
Results: Out of 216 subjects, 121 (56%) had high negative impact, 74 (34.3%) had moderately negative impact on their occupation during COVID-19 pandemic. Among the study participants, 26 (12%) were not willing to seek health care for their illness with reasons being no trust on healthcare facility and belief of fishermen are naturally immune to any infections. A statistically significant association was reported between the knowledge and practice (r-0.518, p value-0.000).
Conclusion: The fishermen community were having high negative occupational impact during COVID-19 pandemic.
Recommendation: Awareness can be created about COVID-19 transmission to improve their knowledge, practice of healthy habits and their health seeking behaviour.
Fishermen • Occupational impact • Health seeking behavior • COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic was an unanticipated occurrence that had a significant impact on people's lives and way of life. Due to this epidemic, a national lockdown was first implemented for three weeks, from March 24 to April 14, 2020, and subsequently, it was prolonged up to May 3, 2020. The implementation of a curfew to stop the spread of COVID-19 had a significant impact on numerous professions, including fishing. Despite being surrounded by metropolitan areas; the fishermen's community has distinct folksociety traits [1]. Since a significant amount of a fisherman's life is spent at sea, their primary source of income and means of subsistence are dependent on fishing and jobs linked to fishing [2]. Their line of work has been significantly impacted by the ongoing restrictions and the enforcement of a nationwide lockdown. The lack of transportation services prevented the sale of the fish that were caught. It had a significant influence on the community of fishermen both professionally and economically. As they have a distinctive folk trait, little research has been done on their understanding of COVID-19, attitudes towards it, or health-seeking behaviours. There is a lack of research on their knowledge, attitude, and practice of healthy habits in preventing COVID-19 transmission and their health seeking behaviour, so this study was intended to evaluate the occupational impact of COVID-19 as well as their knowledge, attitude, practice of healthy habits in preventing COVID-19 transmission, and health seeking behaviour during this COVID-19 pandemic.
This community based cross-sectional study was conducted among the residents of fishermen community in the Puducherry district. Sample size was estimated as 216 considering the that 50% of the participants were preoccupied with COVID-19. The participants were recruited through simple random sampling technique from the selected fishermen community [3]. After obtaining necessary permissions from institutional ethical committee the participants of fishermen community were involved in the study. Participants who are not willing to participates and whose occupation is not fishing or selling were excluded from the study. The details of participant’s socio-demographic variables, occupational impact, knowledge, attitude, practices towards prevention of COVID-19 and their health seeking behavior were obtained using a semi-structured questionnaire after obtaining the informed written consent. The data were collected for a period of 3 months, entered in epicollect 5 exported to MS excel 2020 and analyzed using SPSS v16. The continuous and categorical variables were represented as median (IQR) and frequency (proportions) respectively. The relationship between knowledge, attitude and health seeking behavior was determined using spearman correlation (Figure 1) [4].
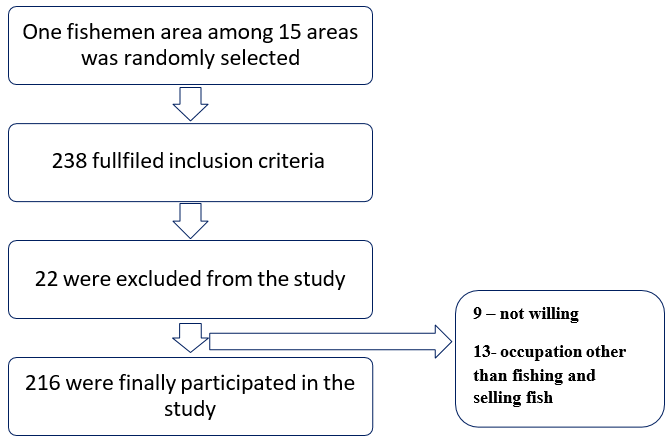
Figure 1. The relationship between knowledge, attitude and health seeking behavior.
A total of 216 participants were participated in the study and the results were described under the following headings:
Sociodemographic details
Among the study participant’s majority (44.4%) of them were aged between 30 to 50 years. Other sociodemographic details of the study participants are given in Table 1 [5].
| Socio demographic details | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 124 (57.4%) |
| Female | 92 (42.6%) |
| Age | |
| 15-30 years | 59 (27.3%) |
| 30-50 years | 96 (44.4%) |
| >50 years | 61 (28.2%) |
| Type of occupation | |
| Fishing | 123 (56.9%) |
| Selling | 93 (43.1%) |
Table 1. Socio demographic characteristics of the study participants (N=216).
Occupational impact and KAP about prevention of COVID-19 transmission
Pretested questionnaire was used to analyze the occupational impact occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic restrictions, knowledge, attitude and practice regarding COVID-19 disease transmission. Higher proportion of study participants (90.2%) had negative occupational impact during the COVID-19 pandemic restrictions.
Majority of the participants (76.9%) had inadequate knowledge about COVID-19 pandemic during the early phase of disease outbreak. About 46.8% and 58.8% of the study participants were having positive attitude and good practice towards prevention of COVID-19 disease transmission. (Table 2) [6].
| Occupational impact | Frequency (Percentage) |
|---|---|
| High negative impact | 121 (56.0%) |
| Moderate negative impact | 74 (34.2%) |
| No impact | 9 (4.2%) |
| Positive impact | 12 (5.6%) |
| Total | 216 (100.0%) |
| Knowledge | |
| Inadequate knowledge | 166 (76.9%) |
| Moderately adequate | 48 (22.2%) |
| Adequate | 2 (0.9%) |
| Total | 216 (100.0%) |
| Attitude | |
| Negative attitude | 28 (13.0%) |
| Neutral attitude | 87 (40.3%) |
| Positive attitude | 101 (46.8%) |
| Total | 216 (100.0%) |
| Practice | |
| Good | 127 (58.8%) |
| Bad | 89 (41.2%) |
| Total | 216 (100.0%) |
Table 2. Occupational impact and KAP about COVID-19 (N=216).
Health seeking behaviour of the study participants
Questions were asked regarding the health seeking behavior of fishermen community were asked. About 88% of the participants seeks medical care however, 85.2% of the participants will not seek health care on same day of development of illness (Table 3). Reasons for not seeking health care among the fishermen community was that they believe that they are having high immunity (Figure 2).
| S. no. | Variables | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Will you get medical treatment for your illness? | Yes | No |
| 190 (88%) | 26 (12%) | ||
| 2 | Will you seek medical treatment on the same day of development of symptoms? | Yes | No |
| 32 (14.8%) | 184 (85.2%) | ||
Table 3. Health seeking behavior of the study participants.
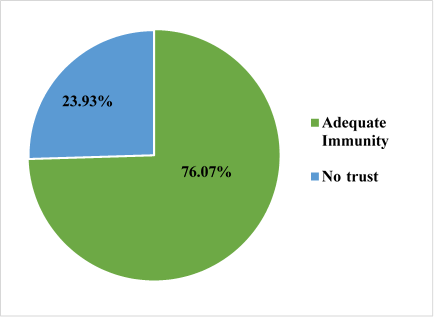
Figure 2. Reason for not seeking health care among fishermen community.
Correlation between knowledge, attitude, practice and health seeking behaviour
Correlation was done between the knowledge about COVID-19, attitude, practice in preventing COVID disease transmission and health seeking behavior. Positive correlation exists between knowledge and practice, attitude and practice, attitude and health seeking behavior (Table 4).
| Knowledge | Attitude | Practice | Health seeking behavior | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge | Correlation coefficient | 1 | |||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | ||||
| Attitude | Correlation coefficient | -0.03 | 1 | ||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.657 | . | |||
| Practice | Correlation coefficient | .191** | .253** | 1 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.005 | 0 | . | ||
| Health seeking behavior | Correlation coefficient | 0.002 | .179** | -0.008 | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.971 | 0.008 | 0.904 | . | |
| **: Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). *: Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). |
|||||
Table 4. Correlation between knowledge, attitude, practice and health seeking behaviour (N=216).
The present community based cross-sectional study was conducted among the fishermen community Puducherry district over a period of 3 months with the aim of assessing the occupational impact during COVID-19 pandemic, their knowledge, attitude, practice towards COVID-19 disease transmission and health seeking behavior.
The present study found that the COVID-19 pandemic and restrictions had a higher negative impact of 90.3% on their occupation. Similar findings were reported by the study done on impact of COVID-19 on commercial fisheries workers in USA found that 95% decline of fish selling during lockdown [7].
In our study, 76.9% of the study participants had inadequate knowledge, 46.8% had good attitude and half of the study population had poor practices to prevent COVID-19. Likewise, a study on KAP of general public towards COVID-19 in India reported that 63.5% of the participants had good knowledge, 74% had a positive attitude and 93.2%of the participants had adopted practices to prevent COVID-19 [8].
The health seeking behaviour the fishermen community during COVID-19 was good (88%) and most of them prefer government facility for their health needs. However, because of fear of isolation, fear of contracting COVID infection and long waiting time majority of the study participants (85.2%) were not seeking health care on the same day of development of symptoms. Among those who does not seek health care, believed that the fishermen were naturally having higher immunity compared to general population.
The fishermen community were having high negative occupational impact during COVID-19 pandemic. Their attitude and practice towards prevention COVID-19 transmission was not much effective. Health education and counselling about COVID-19 transmission to improve their knowledge, practice of healthy habits and their health seeking behavior health problems in the fishermen community.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Citation: Divyabharathy R, et al. "Occupational Impact and Health Seeking Behavior among Fishermen Community During COVID-19 Pandemic in Puducherry: A Community Based Cross-Sectional Study". Prim Health Care, 2025, 15(1), 1-4.
Received: 09-Nov-2023, Manuscript No. JPHC-23-119726; Editor assigned: 11-Nov-2023, Pre QC No. JPHC-23-119726 (PQ); Reviewed: 25-Nov-2023, QC No. JPHC-23-119726; Revised: 03-Jan-2025, Manuscript No. JPHC-23-119726 (R); Published: 13-Jan-2025, DOI: 10.35248/2167-1079.24.15(1). 001
Copyright: © 2025 Divyabharathy R, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.