Research - (2023) Volume 8, Issue 3
Aim of this work is to search and analyze scientific literature involved in the effect played by wireless comunication radiation in the S.A.R.S.-COV-2 spike protein derivates pathological process. This make possible to verify if it is necessary to be considered as a toxicological co-factor. Various published evidence finded graphene impurity in vial some C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine (P. Campra) or in vaccinated blood But It is relevant to deeply investigate this phenomena using scientifc evidence and other interesting documents from independed reseacher useful to generate hypotesys to be confirmed . Crucial also to verify the subpopulation distribution of pathological event in vaccinated like pericarditys or central nervous system thrombosys as well as the use of some technological tool like smartphone in the various age classes. This method make possible to generate hypotesys to be better veriefied . Related the profile of some toxicological aspect of some C.O.V.I.D. -19 vaccine and in specifc way to the rare effect like pericarditis or trombosys are reported in this work some relevant literature involved in the effect played by the SPIKE PROTEINS and its link on epithelial tissue ACE receptor, the Graphene (if present) and under some magnetic field or electrical condition. An experimental hypotesys is submitted to the reseacher in order to produce a global conclusion of toxicological interest in this work is used a neutral approch without pre-concept.
Wireless Communications Radiation (W.C.R.) • Spike protein • ACE receptor • Temperature • Epidemiology • Publich health • C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine • Graphene • Electric Charge • Electromagnetic field • Magnetism • Pathology • Toxicology • Sinergy
Aim of this work is to evaluate the effect played by electro-magnetic field on the complex S.A.R.S. COV-2 SPIKE protein- ACE before the epithelial cell intake and also in presence of graphene. Great part of the pathological effect of the C.O.V.I.D.-19 disease is due by the interaction of the S.A.R.S. cov-2 SPIKE Protein with the ACE 2 receptor and related cellular intake.
(Mainly pulmonary inflamation and coagulopathy, great increase in inflamatory molecule since ARDS and fibrosys: comorbidity and age > 50 years produce the more severe effect as reported in literature) (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
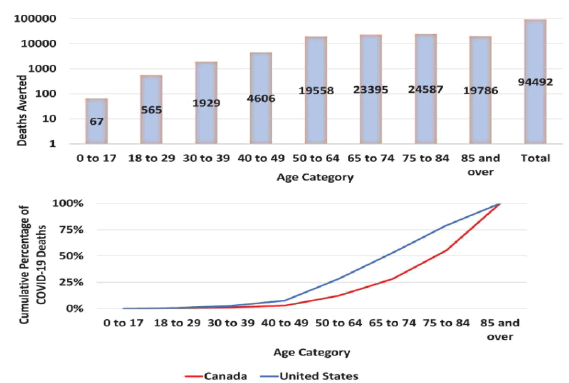
Figure 1: Cumulative counted C.O.V.I.D.-19 deaths averted in Canada as of May 2022 by outperforming the US pandemic response. (A) Absolute deaths averted, by age group and overall; log scale. (B) Cumulative proportion of deaths by age group in Canada, and with a Canada-stand. US pandemic response. Estimates are based on direct standardization.
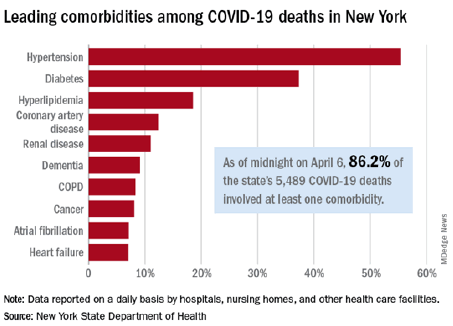
Figure 2: New york C.O.V.I.D.-19 deaths
Of great interest to verify in scientific literature epidemiology ( histograms) of some characteristic event related C.O.V.I.D.-19 disease or Vaccination : pericarditys / myocarditis and CNS thrombosis. Lancet. Risk of myocarditis and pericarditis after the C.O.V.I.D.-19 mRNA vaccination in the USA: a cohort study in claims databases Hui-Lee Wong et al “An increased risk of myo-carditis or peri-carditis was observed after C.O.V.I.D.-19 mRNA vaccination and was highest in men aged 18-25 years after a 2 nd dose of the vaccine. The incidence was rare.” And in article is reported: Comparative Study Vaccine (Figure 3).
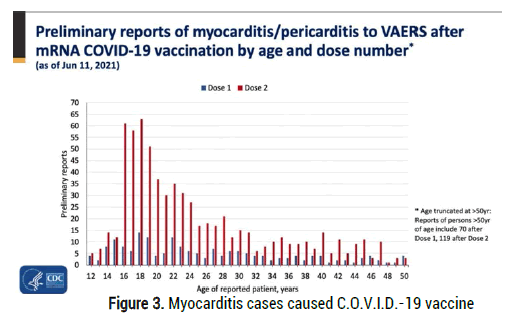
Figure 3: Myocarditis cases caused C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine
Myocarditis and/or pericarditis risk after mRNA C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination: A Canadian head to head comparison of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines Natalia Abraham et al “The risk of myocarditis and/or pericarditis is higher after mRNA-1723 vaccination than the BNT162b2 vaccination in those aged 18-39 years, especially in the males aged 18-29 years, where the risk is several times higher” (Figure 4).
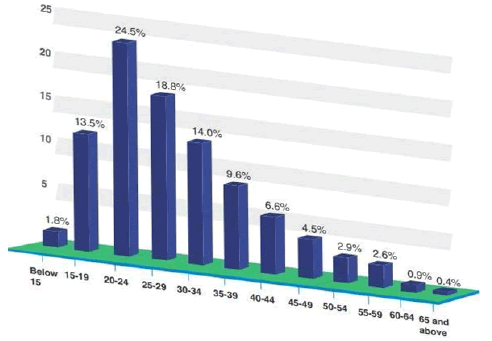
Figure 4: Percentage of Smartphone Users by Age Category.
Also of great interest is to verify the distribution by age class in the use of smarthphone:
And observing: 24 March 2021 EMA/PRAC/157045/2021
Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) Signal assessment report on embolic and thrombotic events (SMQ) with C.O.V.I.D.-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant]) – C.O.V.I.D.-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca (Other viral vaccines) “A combination of blood clots BC and low level of platelets (ptl) , in some cases together with bleeding, has been observed very rarely following vaccination with the C.O.V.I.D.-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca. This included some severe cases with blood clots BC in different or unusual locations and excessive clotting or bleeding throughout the body.
The majority of these cases occurred within the first 7 to 14 days following vaccination and mostly occurred in women under 55 years of age, more women under 55 received the vaccine than other people. Some cases had a fatal outcome” (Figure 5).
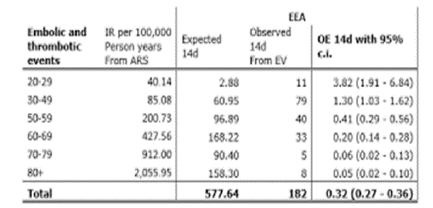
Figure 5: from 24 March 2021 EMA/PRAC/157045/2021 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) Signal assessment report on the embolic and thrombotic events (SMQ) with C.O.V.I.D.-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant]) â?? C.O.V.I.D.-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca (Other viral vaccines)
Related the need to verify if there are or not relationship it is crucial to perform a review of scientific work published by reveiwer boards about this topic. After this phases is submitted to the researcher an experimental project hypotesys in order to produce a global conclusion (Figure 6 and Figure 7).
Figure 6: Cell phone radiation
Figure 7: Everything you need to know about 5g and health
Spike conformation transition in S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 infection Luo L, Zuo Y Preprint from arXiv “The host-cell receptors for S.A.R.S.-CoV and MERSCoV are ACE2 and DPP4 respectively . Recent advances in cryo-electron microscopy characterization of the spike protein SP revealed that the R.B.D.s adopted at least 2 distinct conformations. R.B.D. can be either in the open or in the closed position (called up or down conformation respectively).In the up conformation, the R.B.D. jut out away from the rest of S, such that they can easily bind with the ACE2. In the down conformation the R.B.D.s are tightly packed, preventing binding by ACE2. The receptorbinding event may trap the R.B.D. in the less-stable up conformation, leading to destabilization of S1,triggering conformational change of S2 from prefusion to postfusion state and initiating the membrane fusion. The S.A.R.S.-CoV cell entry also depends on transmembrane protease serine 2 which help to cut S to units S1 and S2. A theory on the conformation transition for S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike protein SP (S) is proposed. The conformation equilibrium between open (up) and closed (down) conformations of receptor binding domain of the spike P is studied from the first-principle. The conformational state population is deduced from the free energy change in conformation transition of Spike protein. We demonstrated that the free energy includes 2 parts, one from the multi-minima of conformational potential and another from the variation of structural elasticity.
Both factors are dependent of amino acid AA mutation. The former is related to the change of affinity of R.B.D. to ACE 2 due to the mutation in the subdomain R.B.M (Receptor Binding Motif) of R.B.D.. The latter is caused by the change of elastic energy of Sipke protein. When the affinity has increased significantly and/or the elastic energy has been reduced substantially the equilibrium is biased to the open conformation. Only then can the virus infection process continue. Possible new S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 variants from A.A mutations in 5-9 sites on R.B.D. interface are predicted. The elastic energy variation needed for conformation transition is estimated in quantitatively way. Taking the elastic-structural change into account more virus variants are possible. Both the D614G mutation, the K986P mutation and the new variants 501Y in current S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 pandemic can be interpreted by the presented theory. The comparison of the infectivity of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 with S.A.R.S.-CoV-1 is made from the point of conformation equilibrium. Why the virus entrance takes priority in lower temperature and higher humidity is interpreted by this present theory. The conformational transition influenced by electromagnetic field is discussed. As in Fig reported there is a potential barrier between 2 conformations. The transmission coefficient is dependent of the height and width of the potential barrier PB . Introducing an electric field will change the conformational barrier of the spike P effectively and in turn change the conformational state population. It was reported that as the electric field increases beyond 0.02 au, the net electron density starts to move from C-H bond towards the carbon C, causing the bond to begin to weaken and lengthen. The static electric field of appropriate strength and direction can break some H-bond and salt bond in the spike and changes the conformation equilibrium of R.B.D.The geomagnetic field GF can effectively block the bombardment of high-energy charged particles in the cosmic ray. Due to the abnormal macula activity the weakened geo-magnetic field would make the spike susceptible to bombardment, causing the residue deletion or amino acid mutation and changing the conformational state population.” (Figure 8).
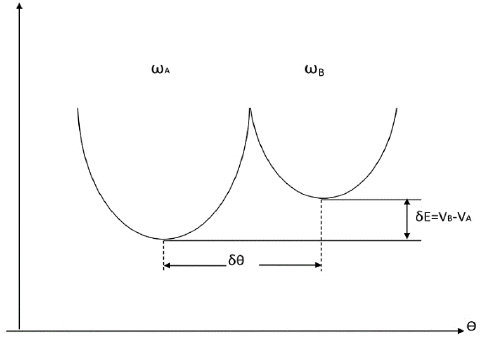
Figure 8: The conformation transition of R.B.D. The closed/open transition of R.B.D. proceeds in 2 directions the equilibrium of which determines the first step of the viral infection.
(Figure 9) from Luo L, Zuo Y: Eq (1) describes the conformation transition of R.B.D.. The closed/open transition of R.B.D. proceeds in 2 directions the equilibrium of which determines the first step of the viral infection. We shall study the conformation equilibrium between the R.B.D.(closed) and the R.B.D.(open). Suppose A denotes closed conformation and B open conformation. The Gibbs free energy is expressed by the GA and GB respectively in 2 conformations. If GA is lower than the GB, then S1 takes an inactive conformation 2 minima separated by a potential barrier represent 2 conformations A (left) and B (right) of R.B.D., 9 is conformational coordinate, ω – the frequency parameter and I – the inertia parameter describing the vibration around the minimum. The molecule may locate in conformation A or B. The conformational state population is determined by 1 factor: the conformational energy Econf=VB-VA and the elastic energy Eelas=kBTlnYA/B. The elastic energy EE is related to the frequency-ratio ωB/ωA or frequency-difference ωB-ωA. As VA
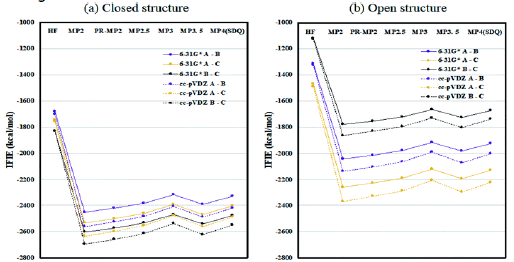
Figure 9: Inter-chain IFIE inter-fragment interaction energies sums (a) for the closed structure (6VXX) and (b) for the open structure (6VYB). Interaction analyses of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike protein based on fragment molecular orbital calculations.
Of interest to observe also some independent reseacher works: (scientific not reviewed, personal opinion):
From Unvaccinated Blood Unrecognizable After Application Of Low Level Electrical Current And Structures Rapidly Grow - Clifford Carnicom's Findings Confirmed Ana Maria Mihalcea, MD, PhD Mar 19 “C. Carnicom showed last year that in four unvaccinated people not only did they have abnormal rouleaux formation ( stacking of red blood cells RBC) - but after applying an extremely low voltage current, the same structures I see in everyone appeared. My findings were confirmed by Dr. D. Nixon in Australia in live blood of vaccinated and unvaccinated people. Around the world, people have called this Graphene Oxide - they see what we see, long Ribbon structures. Calling this Graphene Oxide GO may be a misnomer of the Hydrogel Polymer which encapsulates the payload within the shots - it can be mRNA, toxins, Quantum dots that magnetically alter the human genetic information by modifying the spin states of subatomic particles. Clifford Carnicom called his findings CBD as mentioned above - Cross Domain Bacteria, his name for Morgellon’s, which is a Hydrogel Polymer synthetic life form with many similarities to what we see in live blood of injected and un injected people since the C19 shot rollout.”
“What Nixon found, and filmed, is bizarre to say the least. Inside a droplet of vaccine are strange mechanical structures. They seem motionless at first but when Nixon used time-lapse photography to condense 48 hours of footage into two minutes, it showed what appear to be mechanical arms assembling and disassembling glowing rectangular structures that look like circuitry and micro chips. These are not ‘manufactured products’ in the CDC’s words because they construct and deconstruct themselves but the formation of the crystals seems to be stimulated by electromagnetic radiation and stops when the slide with the vaccine is shielded by a Faraday bag. Nixon’s findings are similar to those of teams in New Zealand, Germany, Spain and South Korea.”
The Spectator is a weekly British newsmagazine on politics, culture, and current affairs. It was first published in July 1828, making it the oldest surviving weekly magazine in the world. “Dr. Nixon revealed his findings of nanotechnology inside the C.O.V.I.D. injections.He also discussed how protecting the vials inside a Faraday bag stopped the structures from forming. A Faraday bag is used to block out electromagnetic radiation; e.g., signals sent between cell phones.”
“Evidence including images of the “vaccine” vials’ contents taken using both an electron microscope, as well as an optical microscope. Now, in a new interview with Maria Zeee, Australia-based Dr. David Nixon shows some of the strangest contents yet in vials of the P.B “vaccine”: micron-scale structures that assemble over time, and seemingly become activated due to ambient Wi-Fi radiation.
In an image taken at 200X magnification (immediately above), Nixon shows a sample of dried-out PB “vaccine” displaying “quite unnatural, rectangular shapes.” Nixon says that when he looked at the same sample the next day, a new structure had appeared (Figure 10).
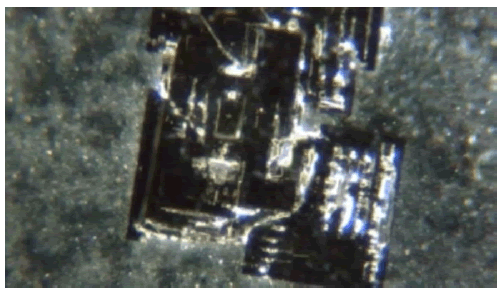
Figure 10: Nixon shows images of a slide of the â??vaccineâ? left out underneath a microscope overnight, versus one kept in a Faraday bag for the same time period.
(As Nixon notes, a Faraday bag is used to block out electromagnetic radiation; e.g. signals sent between cell phones.) The sample that was left out, Nixon says, “grew structures overnight.” He adds, however, “that the (sample) that was sealed (in the Faraday bag) did not grow these structures.”It was a pretty stark contrast that, when the slide was exposed to the wireless router, these structures appeared the next day, and when it wasn’t, all I got was blobs,” Nixon says. The physician adds that he ran his experiment four times, and was never able to get the same kinds of structures that developed outside of the Faraday bag to develop inside of the Faraday bag (Figure 11).
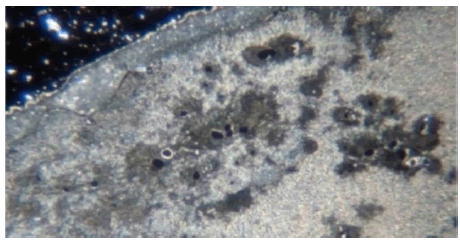
Figure 11: When the wireless router was turned off, was tha, the router was the main source that was affecting the development of the structures.
“It seemed to be, from what happened when the wireless router was turned off, was that… the router was the main source that was affecting (the development of the structures),” Nixon says.”
“Dr Neil points to the report published last August by Dr Phillip M. Altman, a clinical trial and pharmaceutical regulatory affairs consultant (B pharm. Hons), MSc, PhD Clinical Trial & Pharmaceutical Regulatory Affairs Consultant). The report – endorsed by Professor Wendy Hoy, Director of the Centre for Chronic Disease, Univ. of Queensland – argues that C. vaccines are not really vaccines, but experimental gene-based therapies, and have been associated worldwide “with far more deaths, illnesses, injuries, and disabilities than any other therapeutic agent in the history of medicine”.
The lancet Infectious disease
Global impact of the first year of C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination: a mathematical modelling study Oliver J Watson.“Overall, the estimated deaths averted per capita were highest in the high-income countries, reflecting the earlier and wider roll-out of vaccination campaigns . We estimated that more deaths were averted in the W.H.O. European region ER. This was due to both the greater number of vaccinations administered in these kind of regions and the higher levels of vaccine coverage achieved before the arrival of the delta variant.”
With an observational methods various relevant reference related the argument of investigation are reported and the analyzed. All literature comes from scientific database like PUBMED and other are also reported experience by some independent reseacher (scientific works) useful to generate hypotesys to be verified .
Various images , tables and other data are reported to help in this evaluation after this an experimental project hypotesys is submitted to the reseracher in order to provide in order to test hypotesys of relationship and its intensity (statistical, clinical). Additionally also some documents are reported (some study of low level of quality or white paper) in order to Produce hypotesys of work to be verified according the scientific criteria of reproducibility and accurancy.
Evidence for a connection between coronavirus disease-19 and exposure to radiofrequency radiation from wireless communications including 5G Beverly Rubik , R. R. Brown “both C.O.V.I.D.-19 and W.C.R. exposure can affect the heart and cardiovascular CV system, directly and/or indirectly. S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 inhibits intrinsic pathways designed to reduce R.O.S levels, thereby increasing morbidity. Immune dysregulation, that is, the upregulation of IL-6 and TNF-α and suppression of IFN α and IFN β have been identified in the cytokine storm accompanying severe C.O.V.I.D.-19 infections and generates oxidative stress OS. Oxidative stress OS and mitochondrial dysfunction may further perpetuate the cytokine storm, worsening tissue damage, and increasing the risk of severe illness and death [1].
Similarly low-level W.C.R. generates R.O.S in cells that cause oxidative damage. Oxidative stress is considered to be one of the primary mechanisms in which W.C.R. exposure causes cellular damage. Among about 100 currently available peer-reviewed studies investigating oxidative effects of low-intensity W.C.R., 93 of these studies confirmed that W.C.R. induces oxidative effects in biological systems. W.C.R. is an oxidative agent OA with a high pathogenic potential especially when exposure is continuous .
Oxidative Stress (OS) is also an accepted mechanism causing endothelial damage . This may manifest in patients with severe C.O.V.I.D.-19 in addition to increasing the risk for Blood Clot (BC) formation and worsening hypoxemia. Low levels of the glutathione, the master antioxidant, have been observed in a small group of C.O.V.I.D.-19 patients, with the lowest level found in the most severe cases. The finding of low glutathione levels in these patients further supports oxidative stress as a component of this disease. In fact, glutathione, the major source of sulfhydryl-based antioxidant activity in the human body, may be pivotal in C.O.V.I.D.-19 .The Glutathione deficiency has been proposed as the most likely cause of serious manifestations in C.O.V.I.D.-19 disease. The most common co-morbidities, hypertension; obesity; diabetes; and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease support the concept that pre-existing conditions causing low levels of glutathione may work synergistically to create the “perfect storm” for both the respiratory and the vascular complications of severe infection. Another paper citing 2 cases of C.O.V.I.D.-19 pneumonia treated successfully with the intravenous glutathione also supports this hypothesis. Many studies report oxidative stress OS in humans exposed to W.C.R.. Peraica et al. found diminished blood levels of the glutathione in workers exposed to W.C.R. from radar equipment (0.01 mW/cm2 – 10 mW/cm2; 1.5 – 10.9 GHz). Garaj-Vrhovac studied bioeffects following exposure to non-thermal pulsed microwaves MW from marine radar (3 GHz, 5.5 GHz, and 9.4 GHz) and reported a reduced glutathione levels and increased Malondialdehyde (MD) (marker for oxidative stress OS ) in an occupationally exposed group . Blood plasma of individuals residing near mobile phone base stations showed significantly reduced glutathione, catalase, and superoxide dismutase levels over unexposed controls.
In a study on human exposure to W.C.R. from mobile phones, increased blood levels of Lipid Peroxide (LP) were reported, while enzymatic activities of superoxide Dismutase (SD) and glutathione peroxidase in the red blood cells decreased, indicating an oxidative stress. In a study work on rats exposed to 2450 MHz (wireless router frequency), Oxidative Stress (OS) was implicated in causing red blood cell BC lysis (hemolysis) . In another work, rats exposed to 945 MHz (base station frequency) at 0.367 mW/cm2 for 7 h/day, over 8 days, demonstrated low glutathione levels and increased malondialdehyde and Superoxide Dismutase (SD) enzyme activity, hallmarks for oxidative stress . In a long-term controlled study on rats exposed to 900 MHz (mobile phone frequency) at 0.0782 mW/cm2 for 2 h/day for 10 months, there was a significant increase in malon-dialdehyde MD and total oxidant status over controls . In another long-term controlled study on rats exposed to 2 mobile phone frequencies, 1800 MHz and 2100 MHz, at power densities 0.04 – 0.127 mW/cm2 for 2 h/day over 7 months, significant alterations in oxidant-antioxidant parameters, D.N.A strand breaks, and oxidative DNA damage were found.
There is a correlation between oxidative stress and thrombogenesis. R.O.S can cause endothelial dysfunction and cellular damage. The endothelial lining of the vascular system contains ACE2 rec. that are targeted by S.A.R.S.-CoV-2. The resulting endotheliitis can cause luminal narrowing and result in diminished blood flow to downstream structures. Thrombi in arterial structures can further obstruct Blood Flow (BF) causing ischemia and/or infarcts in the involved organs, including pulmonary emboli and strokes. Abnormal blood coagulation leading to micro-emboli was a recognized complication early in the history of C.O.V.I.D.-19 . Out of 184 ICU C.O.V.I.D.-19 patients, 31% showed thrombotic complications . Cardiovascular CV clotting events are a common cause of C.O.V.I.D.-19 deaths . Pulmonary embolism PE, disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (IC) , liver, cardiac, and renal failure have all been observed in C.O.V.I.D.-19 patients”[1].
Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology, The toxic effect of mobile phone radiation on rabbit organs. “Whether electromagnetic radiation ER emitted from mobile phones is hazardous to human health is largely unknown. We investigated the effects of the mobile phone radiation on critical organs in a rabbit model by exposing the animals to mobile phone radiation with subthermal specific absorption rate (SAR) of 1.0 and 0.7 W/kg for the head and the body, respectively, for about 16 weeks (6 h/day, 6 days/week). There is no apparent change at the organ level. H&E staining showed that radiationexposure significantly increased inflammatory cell infiltration in the liver and the lungs with a lesser degree of myocardial cell cytoplasmic vacuolation (Figure 12). Results from γ-H2AX staining suggest that radiation can also cause D.N.A damage in the brain. No apparent activation of Caspase-3 in the organs examined. Our data suggest that mobile phone radiation may be more hazardous to both the liver and the lungs, and less toxic to the brain and heart” [2].
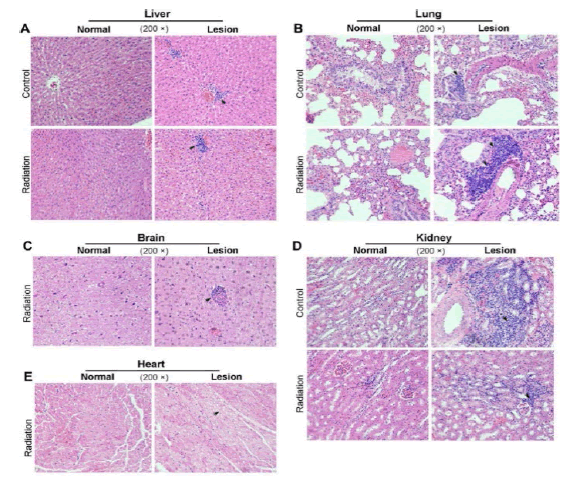
Figure 12: Histopathology analysis of the rabbit tissues after 16 weeksmobile phone radiation. Rabbit tissues were analyzed by H&E staining. Radiation, rabbits exposed to the mobile phone radiation. Control, rabbits without exposure to mobile phone radiation MPR . Normal/Lesion, normal or lesion tissues observed. Inflammatory cell infiltration (A, B, C, D) and cytoplasmic vacuolation (E) were indicated by black arrows.
Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health David Schuerman: “Concomitant with the ever-expanding use of the electrical appliances and mobile communication systems, public and occupational exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) in the extremely-low-frequency and radiofrequency range has become a widely debated environmental risk factor for health. Radiofrequency (RF) EMF and Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) MF have been classified as possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B) by International Agency for Research on Cancer . The production of reactive oxygen species, potentially leading to cellular or systemic oxidative stress, was frequently found to be influenced by EMF exposure in animals and cells. In this review, we summarize key experimental findings on oxidative stress related to EMF exposure from animal and cell studies of the last decade. The observations are discussed in the context of Molecular Mechanisms (MM) and functionalities relevant to health such as the neurological function, genome stability, immune response, and reproduction. Most animal and many cell studies showed increased oxidative stress caused by RF-EMF and ELF-MF. In order to estimate the risk for human health by manmade exposure, experimental studies in humans and epidemiological studies need to be considered as well “ [3]
Effect of Mobile Phone Radiation on Cardiovascular Development of Chick Embryo W Ye F Wang et al “The biological effects on cardiovascular CV development of chicken embryos were examined after radiation exposure using mobile phone (900 MHz; specific absorption rate˜1.07 W/kg) intermittently 3 h per day during the incubation. Samples were selected by morphological and histological methods. The results showed the rate of embryonic mortality EM and cardiac deformity increased significantly in exposed group (P < 0.05)” [4]. (2G, 3G, and 4G networks use frequencies in the UHF or low microwave bands, 600 MHz to 3.5 GHz).
Real-world cell phone radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposures. “In 2011 the IARC classified radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF EMF) from cell phones as possibly carcinogenic to humans. The National Toxicology Program NTP and the Ramazzini Institute have both reported that RF EMF exposures significantly increase gliomas and Schwannomas of the heart in rodent studies” [5].
Establishment of injury models in studies of biological effects induced by microwave radiation.“Cardiac biochemical function indicators used in the studies of microwave-radiation MWR -induced biological injuries mainly included myocardial enzyme spectrum levels and the ion concentrations. It is well known that the activities of myocardial enzymes and the intracellular or extracellular ion concentrations change when the cardio-myocytes are injured and the integrity of the cell membrane is broken. The indicators of the myocardial enzyme spectrum used in previous studies of microwaveradiation-induced cardiac injuries mainly included the levels of L.D.H, creatine kinase , CK-MB) and hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. The most commonly used indicator of ion concentration was the Ca2+ level of ventricular myocytes. The heart can secrete various peptide hormones to regulate its own function.The expression of these hormones could also be used to evaluate the state of cardiac endocrine function. The most popular indicator used in studies of microwave-radiation MWR -induced cardiac injury is atrial natriuretic peptide” [6].
Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health “In the heart of Wistar rats, 2.45 GHz RF-EMF exposure for 5 min (50, 100, 150, 200 mW/cm2) or 30 days (SAR: 0.1 W/kg) resulted in changes in R.O.S and oxidative stress markers and increased tissue toxicity and apoptosis or in more lipid peroxidation and reduced S.O.D, respectively . 2 studies in Sprague-Dawley rats examined oxidative stress in the heart applying laboratory-generated 900 MHz RF-EMF signals. After an in utero exposure during gestational days 13–21 at 0.025 W/kg SAR for 1 h/day and examination at postnatal day 21, there were clear indications of oxidative stress OS , tissue toxicity and apoptosis in the heart” [3].
The effects of electromagnetic radiation (2450 MHz wireless devices) on the heart and blood tissue: role of melatonin “In heart tissues, MDA and NO levels significantly increased in group III compared with groups I and II (p < 0.05). Contrary to these oxidant levels, CAT and the SOD enzyme activities decreased significantly in group III compared with the groups I and II (p 0.05)” (Figure 13) [7].
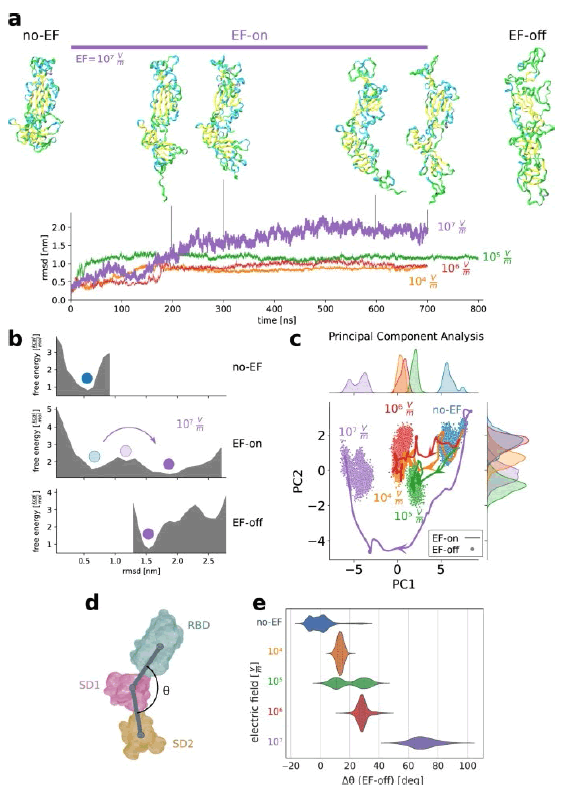
Figure 13: Electric fields are able to induce global conformational changes in the spike glycoprotein SP, affecting the stability of folding states.a, b EF driven major shape changes occur in the different subunits and between subunits of the S protein.
A Snapshots of the studied fragment of S under an EF of 107 V m−1 at 0 ns (initial thermalised stable conformation), 200, 300, 600 and 700 ns, and after EF-off (see text) dynamics during 200 ns. The orientation of the protein is the same in all figures reported .
Trajectories for different electric-field EF strengths are quantified through the root-mean-square-displacement with respect to the initial structure. Snapshots in a correspond to different times along the EF-on trajectory. b Electric fields EF modify the free energy landscape enabling the protein to overcome the potential barriers. Estimated free energy landscape along the thermalisation (no-EF-), EF-on- and EF-off trajectories .
The blue and the light blue dots identify the energy minimum EM of the initial structure before and during EF application. Purple dots correspond to the new minimum reached under the EF, which remains stable after switching off the EF. c Principal component analysis reveals the existence and stable nature of new states after EF application . Discretised trajectories of the EF-on and EF-off runs projected onto a plane defined by the 2 principal components (PC1, 20% of variance; and PC2, 8.2% of variance). Curves on the upper and the right axis show the density of points along PC1 and PC2. Once the S. protein has found a new equilibrium basin, which is different for each EF intensity, no return to the initial state occurs after switch-off of the EF. Curves in the EF-on trajectories are low-pass filtered using a Gaussian kernel (standard deviation 10 ns). d Field-induced conformational states can be characterised by the angles formed by the vectors connecting the centroids of clustered residues. e Violin plot of the distributions of the shift â?³θ of the angle θ for different field intensities (EFoff runs) with respect to a no-EF representative structure. â?³θ is suitable to describe the unfolding of the domain SD2 observed in a. In the violin plot, the central line indicates the median, while left and right lines indicate lower and upper quartiles. EF intensities are color-coded equally for all subfigures.
The S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike protein is vulnerable to moderate electric fields “The spike protein SP of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 (and especially R.B.D.) is unusually vulnerable to external electric fields. Results of Fig. reported show that the ensuing states under EF application clearly represent distinct atomic rearrangements depending on field strength. This raises the question whether tailored EF could be designed in order to drive SPIKE P towards desired target structural states. Pulse trains, like those used in the food industry, or shaped oscillatory EFs of variable central frequency, envelope, duration and polarisation, could be optimised to promote a selective structural response in a similar way as in concepts involving electromagnetic fields” (Figure 14) [8].
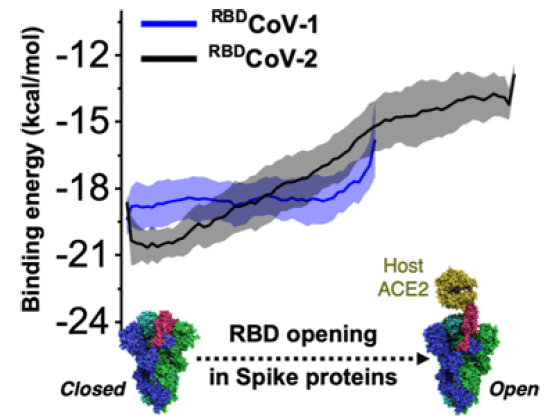
Figure 14: Energetics of Spike Protein Opening of SARS-CoV-1 and SARSCoV-2 and Its Variants of Concern: Implications in Host Receptor Scanning and Transmission
Closed (3down) and open (1 up 2 down) states. Our analysis work in the absence of ACE2 shows that this transition occurs at the energetic cost of breaking very high-frequency contacts between the R.B.D. hinge and the S2 region in chain B and A. The rearrangement of those residues has an energetic cost in the range of 10–15 kcal/mol which is consistent with the PB analysis that quantifies the change in free energy FE on the order about of 10.4 kcal/mol for 3down to 1up2down. Our studies also show the large energetic cost required to transit from closed to 2up1down conformation (~30 kcal/mol) in the absence of the ACE2 receptor which can be associated with mechanical loading and virus-cell collisions at the early stage. This result indicates the propensity of the spike protein SP to likely be found in the 1up2down conformation prior to interacting with the cell surface [9]. And from Cell Phones, Microwave Ovens, and Wi-Fi – Can They Cause Cancer? Ernest L. Lippert “Wi-Fi systems operate in the wavelength range of 6 12 cm. and energy range roughly 0.47 0.24 cal/mole. This is 80,500/0.3 ≈ 270,000 times less than the 80.5 kcal/mole energy required to break the chemical bonds. Cell phones operate with wavelengths in the region of 100 cm (1 m) corresponding to an energy of 2.86E-05 kcal/mole. This is 8.05E+01/2.56E-þ 5≈2,820,000 times less energy than required to break the chemical bonds”
Physical Differences between Man-Made and Cosmic Microwave CM Electromagnetic Radiation and Their Exposure Limits, and Radiofrequencies as Generators of Biotoxic Free Radicals. “Given that adiabatic tunnelling breaks the electron-proton binding energy in the hydrogen atom and that RF-EMF photons can provide this energy in the 2G–5G range, it can be expected that microwave MW adiabatic tunnelling will provide the cumulative RF photons needed to split the antiparallel spin electron pair holding the O–H bond in H2O of 1.88 eV (117.61 Kcal/mol) , and generate the hydroxyl (•OH) and hydrogen (•H) free radicals. Photons at the 2G–5G spectral range could provide free radicals FR with biological and medical implications for man’s health” (Figure 15) [10].
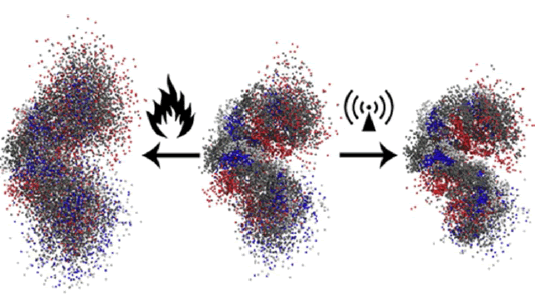
Figure 15: Superpositions of peptide atoms over the entire time span of the trajectory (200 ns). Displayed are structures for simulations at 300 K (middle), conventional heating to 700 K (left), and microwave MW heating to 700 K (right). Tt/Tr are the translational (Tt) and rotational (Tr) temperatures during MD simulations.
Our MD study reveals that continuous microwave irradiation through rotationally hot polar water molecules WM affects the conformational preferences of a small helical β-peptide (Figure 15). Where conventional heating leads to a kind of complete loss of structure, the effects [11].
Non-ionizing radiation: RF energy is identified as non-ionizing radiation. The photon energies of RF electromagnetic waves EW are not adequate to produce the ionization of atoms and molecules. Examples are radio waves, microwaves MW, infrared waves, et other The primary health effect of nonionizing radiation is temperature production in body tissue [12].
Our results have shown for the first time that the Spike protein SP has the possibility to stay in an active and inactive state based on the external temperature. we found that Receptor Binding Motif (R.B.M), present on the R.B.D. of S1, begins to close around temperature of 40°C and attains a completely closed- conformation at 50°C (Figure 16) [13].
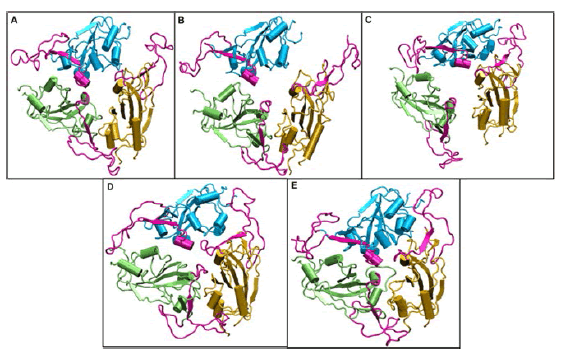
Figure 16: Structures of the receptor binding domain of Spike protein after 200 ns of simulation at different temperatures exhibit diverse structural dynamics. Time-averaged conformations of R.B.D. of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 Spike protein SP at, (A) 10°C, (B) 20°C, (C) 30°C, (D) 40°C, and (E) 50°C. The three chains are colored in lime, cyan, and orange. The receptor binding motif (shown in magenta) is oriented in a confined conformation at higher temperatures.
The nature of the inteaction between SPIKE P and ACE: the protein R.B.D. is attracted by the ACE2 due to their opposite net charges at their binding interfaces and according Ansovini R, Compagnucci L. Use of Polio Vaccine Salk vs S.A.R.S.- CoV-2E and HIV-1E 2, both as Therapeutic Drug and Effective Vaccine to Make Memory-Cells Able to Stop Reinfections. “Dr. Ansovini began studying the viruses by focusing his attention on HIV-1. Themain discovery he made is that this virus, so difficult to treat, can be classified like “electrical”: one of its functional proteins, like “p. 24”, actually has an electrical value, in other words it has a charge, and therefore it is not allosterically neutral as proteins usually are.
Comparison of electrical properties of viruses studied by AC capacitance scanning probe microscopy Robert I MacCuspie , N. Nuraje, Sang-Yup Lee, Anne Runge, H. Matsui “Because those capsid proteins and glyco-proteins GP are characteristic of the virus strain, this kind of technique could be applied to detect and identify viruses at the single viron level using their distinct capacitance spectra like fingerprints without labeling.” and according: The S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 Spike protein has a broad tropism for mammalian ACE2 proteins: “Corona-virus entry into host cells is initiated by direct protein–protein interactions between the virally encoded homotrimeric Spike protein SP, a class I trans-membrane fusion protein found embedded in the virion envelope, and proteinaceous receptors or sugars on the surface of the host cells.”
It is so possible to say that the electrical interaction by the spike protein and ace is a crucial factor that influence the cellular intake with the start of the pathological event related this virus infectious disease. it is of great interest to observe also the research of p campra university of almeira or recent and really interesting new evicence (disinfection ad natura docet darkfield microscope analysis n 1/ 2022 Giovannini F and other research works published also by university professors and other professionals).
All work related the presence of graphene derivates in vials of some C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine or in blood of vaccinated. The electrical properies of graphene and graphene GO are clearly reportend in scientific literature but this impurity in some C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine how can inlfuence the SPIKEACE interaction? And electro magnetic field of various intensity and duration can produce acute/ chronic damage vs normal condition?
According Methods Mol Biol. 2014; Superparamagnetic nanoparticle delivery of D.N.A. vaccine Fatin Nawwab Al-Deen, “The efficiency of delivery of D.N.A. vaccines is often relatively low compared to the protein vaccines. The use of super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles NP to deliver genes via magnetofection shows promise in improving the efficiency of gene delivery both in vitro and in vivo. The duration for the gene transfection especially for in vitro application can be significantly reduced by magnetofection compared to the time required to achieve high gene transfection with standard protocols. SPIONs that have been rendered stable in physiological conditions can be used as both therapeutic/diagnostic agents due to their unique magnetic characteristics. Valuable features of iron oxide nano-particles NP in bio-applications include a tight control over their size distribution, magnetic properties of these particles, and the ability to carry particular biomolecules to specific targets. The internalization and half-life of the particles within the body depend upon the method of synthesis.Various synthesis methods have been used to produce magnetic nano-particles for bio -applications with different sizes and surface charges. The most common method for synthesizing nanometer-sized magnetite Fe3O4 particles in solution is by chemical coprecipitation of iron salts. The coprecipitation method is an effective technique for preparing a stable aqueous dispersions of iron oxide nanoparticles. Here We describe the production of Fe3O4-based SPIONs with high magnetization values (70 emu/g) under 15 kOe of the applied magnetic field MF at room temperature, with 0.01 emu/g remanence via a coprecipitation method in the presence of trisodium citrate as a stabilizer. Naked SPIONs often lack sufficient stability, hydrophilicity, and the capacity to be functionalized. In order to overcome these kind of limitations, polycationic polymer was anchored on the surface of freshly prepared SPIONs by a direct electrostatic attraction between the negatively (-) charged SPIONs (due to the presence of carboxylic groups) and the positively charged polymer. Polyethylen-imine was chosen to modify the surface of SPIONs to assist the delivery of plasmid D.N.A. into mammalian cells due to the polymer's extensive buffering capacity through the "proton sponge" effect” (Figure 17).
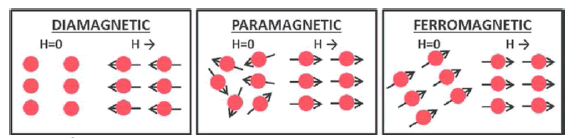
Figure 17: In the absence of a magnetic field, diamagnetic and paramagnetic materials remain non-magnetized on ... [+]leonadro ricotti / v. Iacovacci et al., 2016, in lab-on-a-chip fabrication and application.
Nanomaterials (Basel), Electrical Property of Graphene and Its Application to Electrochemical Biosensing Jin-Ho Lee, S.-Jeong Park, Jeong-Woo Choi “Graphene, a single 2-dimensional (2D) layer of a hexagonal structure consisting of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms, and its derivatives have received increasing attention in the bio-medical fields, due to its unique physico and chemical properties. This feature includes a high surface area, excellent electrical conductivity, strong mechanical strength, unparalleled thermal conductivity, and ease of surface functionalization” (Figure 18,19).
Figure 18: Magnetic field lines, as illustrated by a bar magnet: a magnetic dipole, with a north and south pole ... [+]Newton Henry Black, Harvey N. Davis (1913) practical physics.
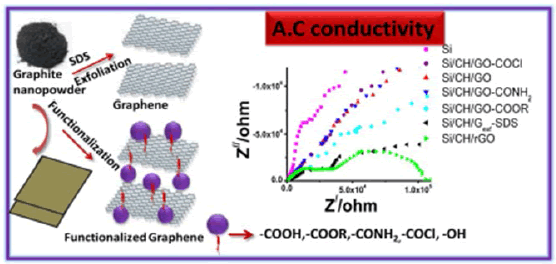
Figure 19: Graphene conductivity
In scientific reports articles article 07 December 2020, Observation of magnetic domains in graphene magnetized by controlling temperature, strain and magnetic field Mahsa Alimohammadian and B.Sohrabi : “Graphene, as a 2D material, is an excellent candidate for replacing many conventional materials in various kind of applications due to remarkable electrical, thermal, mechanical, and optical properties. In the honey- comb structure of the graphene, the presence of one free electron FE per atom is responsible for high electron mobility and the carriers transport is described by Dirac equation.Other electrical properties such as room-temperature quantum Hall effects, unique band structure, and ambipolar electric field effects, covers the electronic application”.
During clinical trials for the vaccines currently deployed in the U. K, no adverse events that match the magnetic phenomenon described were reported. The ‘Information for UK Recipients’ (Pfizer BioNTech/AstraZeneca vac.) and ’Patient Information Leaflet’ (Moderna vac.) provide a list of ingredients for each vaccine. None of these ingredients are considered to cause “magnetism” when administered to a vaccine recipient. “I have evidence of someone displaying magnetism at the site of an injection (given in preparation for travel abroad) at a Boots pharmacy in the East of England prior to Jan 2021. How can this be accounted for? Are the MHRA aware of any other reports of cases of post-injection magnetism prior to the rollout of the C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccines? During clinical trials for the vaccines currently deployed in the UK, no adverse events that match the magnetic phenomenon described were reported. The ‘Information for UK Recipients’ (Pfizer BioNTech/AstraZeneca vac.) and ’Patient Information Leaflet’ (Moderna vaccine) provide a list of ingredients for each vaccine. None of these ingredients are considered to cause “magnetism” when administered to a vaccine recipient.”
In a non published article: (Study on the Electromagnetism of Vaccinated Persons in Luxembourg,
European Forum fo Vaccine Vigilance, Goudjil, 2021) this document it is reported that: The information described as ‘Study on the electromagnetism of vaccinated persons in Luxembourg’ does not appear to have been published in a recognized scientific journal or subjected to peer review. The article does not state which vaccines were given so little can be derived from this information. Study on the Electromagnetism of Vaccinated Persons in Luxembourg, European Forum for Vaccine Vigilance,Mamer and Goudjil. Mr. Amar goudjil, treasurer of the association AEFVV and member in charge of demographic and sociological issues.
That a panel of 200 individuals living or working in Luxembourg would be interviewed. That this panel would be divided into 2 groups. The first would be composed of 100 individuals vaccinated in Luxembourg and the second of 100 unvaccinated individuals for comparison purposes. “Summary presentation of the results for the study week from 1 June to 5 June 2021: Only 30 vaccinated and 30 unvaccinated people were finally interviewed while the target was to interview 100 for the first group and 100 for the second. The condition of gender distribution was met. In each group, 15 women and 15 men were interviewed. In the non-vaccinated group, out of the 30 individuals interviewed, the number of people showing attraction to the magnet was 0 (zero). Therefore the experiment ended there for this group. In the vaccinated group, on the other hand, 29 of the 30 individuals interviewed showed attraction to the magnet. That is, the magnet adhered to their skin without difficulty.” Of these same 29 individuals, 22 have the magnet adhering to only one shoulder and only to the injection area. These 22 individuals are those W.H.O. received only one injection. The other 7 people in this same group have the magnet adhering on both shoulders. It is now the responsibility of toxicologists and pharmacologists to discover the origins and causes of these attractive effects on vaccinated subjects, and it is the responsibility of the guarantors of the health of the citizens of this country to very quickly demand the opening of an enquiry into the exact and real composition of these so-called vaccines” According the survey, of a purely statistical and sociological nature, on this supposed electromagnetic effect, which is the subject of this report, raises at least three important questions and also of interest : operation secret 16’ by operateurs : Dr julien devilleger (Charente, France) as reported in (A questionable study, low scientific?) Researchers: Dr Julien Devilleger, cardiologist and Jessy Duthil, private nurse (Charente, France) from June 11 to July 27, 2021 Statistics: Fisher test (Biostat TGV software) Magnetization research method:
•Coin held between thumb and index finger, with middle finger bent (safely).
•Person standing, arms swinging, dry skin, little hair on the arms, cream cleaned off with water, then skin dried, sweat absorbed by single-use dry towel.
•Coin held at 20 centimetres below the shoulder, lightly touching the skin, without pressing, and sliding from bottom to top up to about 3 finger-widths below the shoulder.
•Technique to be carried out 2 times in a row, in case of magnetization alternately on the left arm/right arm.
•Magnetization if the coin held for at least 10 seconds
The “Secret 16” observational study, carried out by a cardiologist and a nurse from Charente (France), aims to study the magnetization of a one euro coin in 75 patients vaccinated against C.O.V.I.D., in comparison with a control group of 30 unvaccinated people. It finds a much more frequent magnetization of the part in the vaccinated (35/75) compared to the nonvaccinated (2/30), p=0.0027. This magnetization is much more frequent in case of Astra vaccination (17/28 vaccinated) compared to unvaccinated (2/30), p=0.0014. Between June 1 to July 7, 2021, 256 subjects were enrolled in the study. In our population, 148 (57.8%) declined the C.O.V.I.D.19 vaccination and 108 (42.2%) received it. As expected, the age of the of the 108 vaccinated subjects was significantly greater than the nonvaccinated patients for obvious reasons (44.2 ± 17.1 vs 34.2 ± 19.3; p < 0.0001) of the vaccinated patients, 68.5% received the Pfizer vac., 24.1% Moderna, and 7.4% Johnson & Johnson. Demographics of the study population are noted in Tab. reported reviews the results of the nonC.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccinated group (148) versus the C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccinated group (148 vs 108). Magnet and paper clip attachment to the deltoid muscles occurred in most subjects regardless of vaccination status. No statistical differences between the C.O.V.I.D.-19 non-vaccinated and vaccinated groups were observed. Comparison of unvaccinated versus vaccinated groups yielded no significant differences (p > 0.1) in the magnet score of 4/4 (62.8% vs 53.7%); the clip score of 6/6 (54.1% vs 46.5%) and; the field scores of 10/10 (50.0% versus 41.7%) (Figure 20).
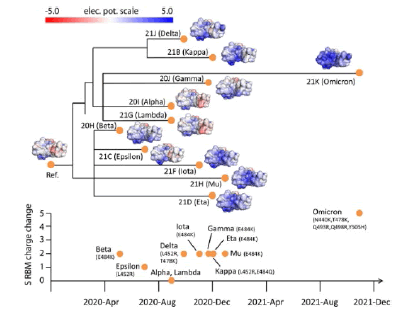
Figure 20: Electrostatic surfaces of Spike R.B.D. variants organized by Nextstrain S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 phylogeny. Tracking of total charge changes with accompanying mutations in SPIKE R.B-M suggests a gradual increase of positive charges over time. The color scale of the electrostatic potential surface is in units of kT/e at T = 37°C.
Front. Virol., 10 June 2022 Sec. Translational Virology ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020 “Our findings reveal that the S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S protein is slightly more positively (+) charged than that of S.A.R.S.-CoV since it contains four more positively charged residues and 5 less negatively charged residues” S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike mR.N.A. vaccine sequences circulate in blood up to 28 days after C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination.
Jan 2023 in Denmark, vaccination against S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 has been with Pfizer-BioNTech (BTN162b2) or Moderna (mR.N.A.-1273) mR.N.A. vac. Patients with chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection followed in our clinic received mR.N.A. vaccinations according to the Danish roll-out vaccination plan. To monitor H.C.V infection, R.N.A. was extracted from patient plasma and R.N.A. sequencing was performed on the Illumina platform. In 10 of 108 HCV patient samples, full-length or traces of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike mR.N.A. vaccine sequences were found in blood up to 28 days after the C.O.V.I.D.19 vaccination. Detection of the mR.N.A vaccine sequences in blood after vaccination adds important knowledge regarding this technology and should lead to further research into the design of lipid-nanoparticles and the halflife of these and mR.N.A. vaccines in humans.” And in article : Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. During the S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 pandemic, novel and traditional vaccine strategies have been deployed globally. We investigated whether antibodies stimulated by mR.N.A. vaccination (BNT162b2), including 3th -dose boosting, differ from those generated by infection or adenoviral (ChAdOx1-S and Gam-C.O.V.I.D.-Vac) or inactivated viral (BBIBP-CorV) vaccines. We analyzed human lymph nodes after infection or mR.N.A. vaccination for correlates of serological differences.
Antibody breadth against viral variants is lower after infection compared with all vaccines evaluated but improves over several months. Viral- variant infection elicits variant-specific antibodies, but prior mR.N.A. vaccination imprints serological responses toward Wuhan-Hu-1 rather than variant antigens. In contrast to disrupted germinal centers in the lymph nodes during infection, mR.N.A. vaccination stimulates robust GCs containing vaccine mR.N.A. and spike antigen up to 8 weeks post-vaccination in some cases. S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 antibody specificity, breadth, and maturation are affected by imprinting from exposure history and distinct histological and antigenic contexts in infection compared with vaccination. Prolonged detection of vaccine mR.N.A. in LN GCs and spike antigen in LN GCs and blood following S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 mR.N.A. vaccination
The bio-distribution, quantity, and persistence of vaccine mR.N.A. and spike antigen after the vaccination and viral antigens after S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 infection are incompletely understood but are likely to be major determinants of immune responses. We performed in situ hybridization with control and S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 vaccine mR.N.A.-specific R.N.A.Scope probes in the core needle biopsies of the ipsilateral axillary LNs that were collected 760 days after the second dose of mR.N.A.-1273 or BNT162b2 vaccination and detected vaccine mR.N.A. collected in the GCs of LNs on days 7, 16, and 37 post-vaccination, with lower but still appreciable specific signal at day 60 . Only rare foci of vaccine mR.N.A. were seen outside of GCs. Axillary LN core needle biopsies of nonvaccinees (n = 3) and C.O.V.I.D.-19 patient specimens were neg. for vaccine probe hybridization. Immunohistochemical staining for spike antigen in mR.N.A.-vaccinated patient LNs varied between individuals but showed abundant spike protein SP in GCs 16 days post-second dose, with spike antigen S.A.still present as late as 60 days post-second dose. Spike antigen localized in a reticular pattern around the GC cells, similar to staining for follicular dendritic cell processes. C.O.V.I.D.-19 patient LNs showed lower quantities of spike antigen but a rare GC had positive staining. Immuno-histochemical staining for N antigen in peribronchial LN secondary and primary follicles of C.O.V.I.D.-19 patients was positive in 5 of the 7 patients, with a mean percentage of nucleocapsid-positive (+) follicles of more than 25% (Figure 21).
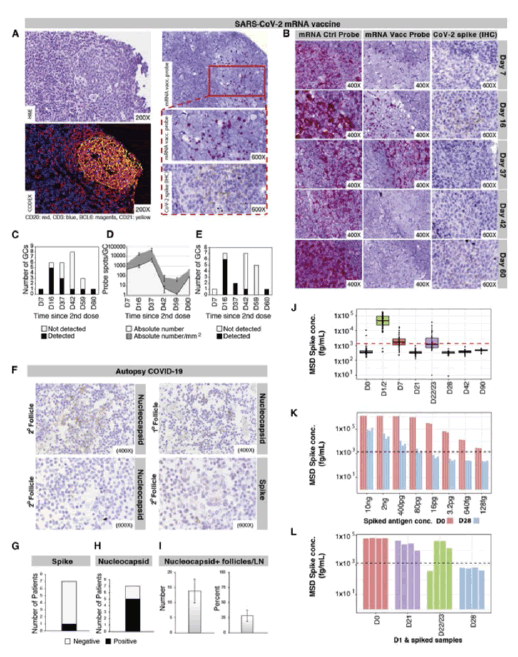
Figure 21: Localization of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 proteins and vaccine mR.N.A. in LNs
Cutting Edge: Circulating Exosomes with C.O.V.I.D. Spike Protein Are Induced by BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of Antibodies: A Novel Mechanism for Immune Activation by mR.N.A. Vaccines Sandhya Bansal. A reference has been published: Comment on “Cutting Edge: Circulating Exosomes with C.O.V.I.D. Spike Protein Are Induced by BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of Antibodies: A Novel Mechanism for Immune Activation by mR.N.A. Vaccines.
S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 causes severe acute respiratory syndrome. mR.N.A. vaccines directed at the S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike protein resulted in development of Abs and protective immunity. To determine the mechanism, we analyzed the kinetics of induction of circulating exosomes with S.A.R.S.CoV-2 spike protein SP and Ab following vaccination of healthy individuals. Results demonstrated induction of circulating exosomes expressing spike protein on day 14 after vaccination followed by Abs 14 d after the second dose. Exosomes with spike protein, Abs to S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike, and T cells secreting IFN-γ and TNF-α increased following the booster dose. Transmission electron TE microscopy of exosomes also demonstrated spike protein Ags on their surface. Exosomes with the spike protein and Abs decreased in parallel after four months. These results demonstrate an important role of circulating exosomes with spike protein for effective immunization following mR.N.A.-based vaccination. This is further documented by induction of humoral and cellular immune responses in mice immunized with exosomes carrying SP.
Science Bulletin Volume 60, Issue 24, Dec. 2015 Front. Immunol., Jan. 2022 Sec. Viral Immunology Persistence of S.A.R.S. CoV-2 S1 Protein in CD16+ Monocytes in Post-Acute Sequelae of C.O.V.I.D.-19 (PASC) up to 15 Months Post-Infection, “The recent C.O.V.I.D.-19 pandemic is a treatment challenge in the acute infection stage but the recognition of chronic C.O.V.I.D.-19 symptoms termed PASC may affect up to 30% of all infected individuals. The underlying mechanism and source of this distinct immunologic condition 3 months or more after initial infection remains elusive.
We investigated the presence of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S1 protein in 46 individuals. We analyzed T-cell, B-cell, and monocytic subsets in both severe C.O.V.I.D.19 patients and in patients with post-acute sequelae of C.O.V.I.D.-19 . The levels of both intermediate (CD14+, CD16+) and non-classical monocyte (CD14Lo, CD16+) were significantly elevated in PASC patients up to 15 months post-acute infection compared to healthy controls (P=0.002 and P=0.01, respectively). A statistically significant number of non-classical monocytes contained S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S1 protein in both severe (P=0.004) and PASC patients (P=0.02) out to 15 months post-infection. Non-classical monocytes were sorted from PASC patients using flow cytometric sorting and the S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S1 protein was confirmed by mass spectrometry- MS . Cells from 4 out of 11 severe C.O.V.I.D.-19 patients and 1 out of 26 PASC patients contained ddPCR+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells PBMC , only fragmented S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 R.N.A. was found in PASC patients. No full length sequences were identified, and no sequences that could account for the observed S1 protein were identified in any patient. That non-classical monocytes may be a source of inflammation in PASC warrants further study. Journal of Clinical Medicine Case Report Bilateral Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion after mR.N.A.-S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 Booster Dose Vaccination Matteo Gironi , Rossella D’Aloisio , T. Verdina , Benjamin Shkurko , Lisa Toto and Rodolfo Mastropasqua “We report a case of a patient with a bilateral branch retinal vein occlusion 24 h after a booster vaccination with the mR.N.A.-1237 vaccine. Fluorescein angiography, performed at three weeks follow-up, showed vascular leakage and blockage, corresponding to hemorrhage areas associated with ischemic areas in the macula and along the arcades involved in the occlusion. The patient was scheduled for urgent injections of intravitreal ranibizumab and laser photocoagulation of the ischemic areas. To the best of our knowledge, this is the 1th case described of concomitant bilateral RVO after C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination. The rapid onset of the side effects in a patient with multiple risk factors for thrombotic events suggests that vulnerable micro-vascular conditions require detailed investigations before administration of a C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine”. Science Bulletin Life & Medical Sciences Magnetogenetics: remote noninvasive magnetic activation of neuronal activity with a magnetoreceptor Xiaoyang Long , Jing Ye , Di Zhao , Sheng-Jia Zhang “Current neuromodulation NM techniques such as optogenetics and deep-brain stimulation are transforming basic and translational neuroscience. These 2 neuromodulation approaches are, invasive since surgical implantation of an optical fiber or wire electrode is required. We have invented a non-invasive magneto-genetics that combines the genetic targeting of a magnetoreceptor with remote magnetic stimulation. The non-invasive activation of neurons was achieved by neuronal expression of an exogenous magnetoreceptor MR , an iron-sulfur cluster assembly protein 1 . In the HEK-293 cells and cultured hippocampal neurons expressing this magneto-receptor, application of an external magnetic field resulted in membrane depolarization and calcium influx in a reproducible and reversible manner, as indicated by the ultrasensitive fluorescent calcium indicator GCaMP6s. the magnetogenetic control of neuronal activity might be dependent on the direction of the magnetic field and exhibits on-response and off-response patterns for the external magnetic field applied. The activation of this kind of magneto-receptor can depolarize the neurons and elicit trains of action potentials, which can be triggered repetitively with a remote magnetic field in W.H.O.le-cell patch-clamp recording. In transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans expressing this magneto-receptor in myo-3-specific muscle cells or mec-4specific neurons, application of the external magnetic field triggered muscle contraction and withdrawal behavior of the worms, indicative of magnetdependent activation of muscle cells and touch receptor neurons. The advantages of the magneto-genetics over optogenetics are its exclusive non-invasive, deep penetration, long-term continuous dosing, unlimited accessibility, spatial uniformity and relative safety. Like optogenetics that has gone through decade-long improvements, magneto-genetics MG , with continuous modification and maturation, will reshape the current landscape of neuro-modulation toolboxes and will have a broad range of applications to basic and translational neuro-science as well as other biological sciences.”
From literature J.of Antimicrobial Agents (2021) Spike S.A.R.S.-COV-2 Protein as Procoagulant Factor and Vaccine Class Effect Hypotesys Luisetto M et al “Binding of virions to integrins on endothelial cells EC could activate angiogenic cell signaling pathways; dysregulate integrinmediated signaling pathways controlling developmental processes; and precipitate endothelial activation to initiate blood clotting. Like a procoagulant state, perhaps together with enhancement of platelet PTL aggregation through virions binding to integ rins on platelets, could amplify the production of micro-thrombi that pose the threat of pulmonary thrombosis and embolism, strokes and other thrombotic consequences. ”There is a similarity in thrombosis due by C.O.V.I.D.-19 and some rare event post some C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination. All this evidence requires to submit a relevant question to the researcher : to use spike protein model to produce a vaccine is really the right solution. It is possible that a class effect can be observed? And before to use this vaccine it is needed to test patient for platelet PTL level, coagulation factor level and first level and second level tests like protein C and S deficiency, factor V Leiden, D-dimer, antithrombin abnormality and other factors that can be relevant (smoke, estrogen - progestin pill, chronic inflammatory disease)”[14].
Luisetto M et al Self-Assembling Property of Graphene Derivates Chemico - Physical and Toxicological Implications. Ann Med Case Rep. 2022 because in toxicology are well known various situation of combined toxic effect by multiple chemical dangerous exposure It is needed to verify the clinical effect of the self-assembling graphene G.O. effect added to spike protein using in vitro sample (Animal model and sample from humans’ specimens: subjects volunteers). The experimental project submitted can help for this scope. It is also of interest to verify if the cumulative effect of this 2 substantia Graphene go and spike protein. Show and added toxic effect (sinergic) or this is greater than the single molecule acting alone and the kinetic related [15].
Multicenter Study Eur Radiol . 2022 July Cardiac magnetic resonance CMR imaging of myocarditis and pericarditis following C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination: a multicenter collection of 27 cases Emanuele Angelo Di Dedda, “To assess clinical and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging features of patients with peri-myocarditis following Coronavirus Disease 2019 (C.O.V.I.D.-19) vaccination. We retrospectively collected a case series of 27 patients W.H.O. underwent CMR in the clinical suspect of heart inflammation following C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination, from 16 large tertiary centers. Our patient's cohort was relatively young (36.6 ± 16.8 years), predominately included males (n = 25/27) with few comorbidities and covered a catchment area of about 8 million vaccinated patients. CMR revealed typical midsubepicardial non-ischemic Late Gadolinium Enhancement (LGE) in 23 cases and matched positively with CMR T2 criteria of myocarditis. In 7 cases, typical hallmarks of acute peri-carditis were present. Short-term follow-up (median = 20 days) from presentation was uneventful for 25/27 patients and unavailable in 2 cases. While establishing a causal relationship between peri-myocardial inflammation and vaccine administration can be challenging, our clinical experience suggests that CMR should be performed for diagnosis confirmation and to drive clinical decision-making and follow-up” [16-21]. (Figure 22). Electrostatic surfaces of S.A.R.S.-CoV S protein R.B.D., S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S protein R.B.D. and ACE2 R.B.D.. (A) Electrostatic surface of S.A.R.S.-CoV S protein R.B.D.; (B) Electrostatic surface of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S protein R.B.D.; (C) Electrostatic difference between S.A.R.S.- CoV and S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S protein R.B.D., by subtracting electrostatic values of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 by S.A.R.S.-CoV, and mapped the values on the surface of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2; (D) Electrostatic surface of human ACE2 R.B.D.; (E) Structure comparison of S.A.R.S.-CoV S protein R.B.D. and S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 S protein R.B.D., colored with purple and yellow, respectively; (F) The structure of human ACE2 binding domain, colored with gray.
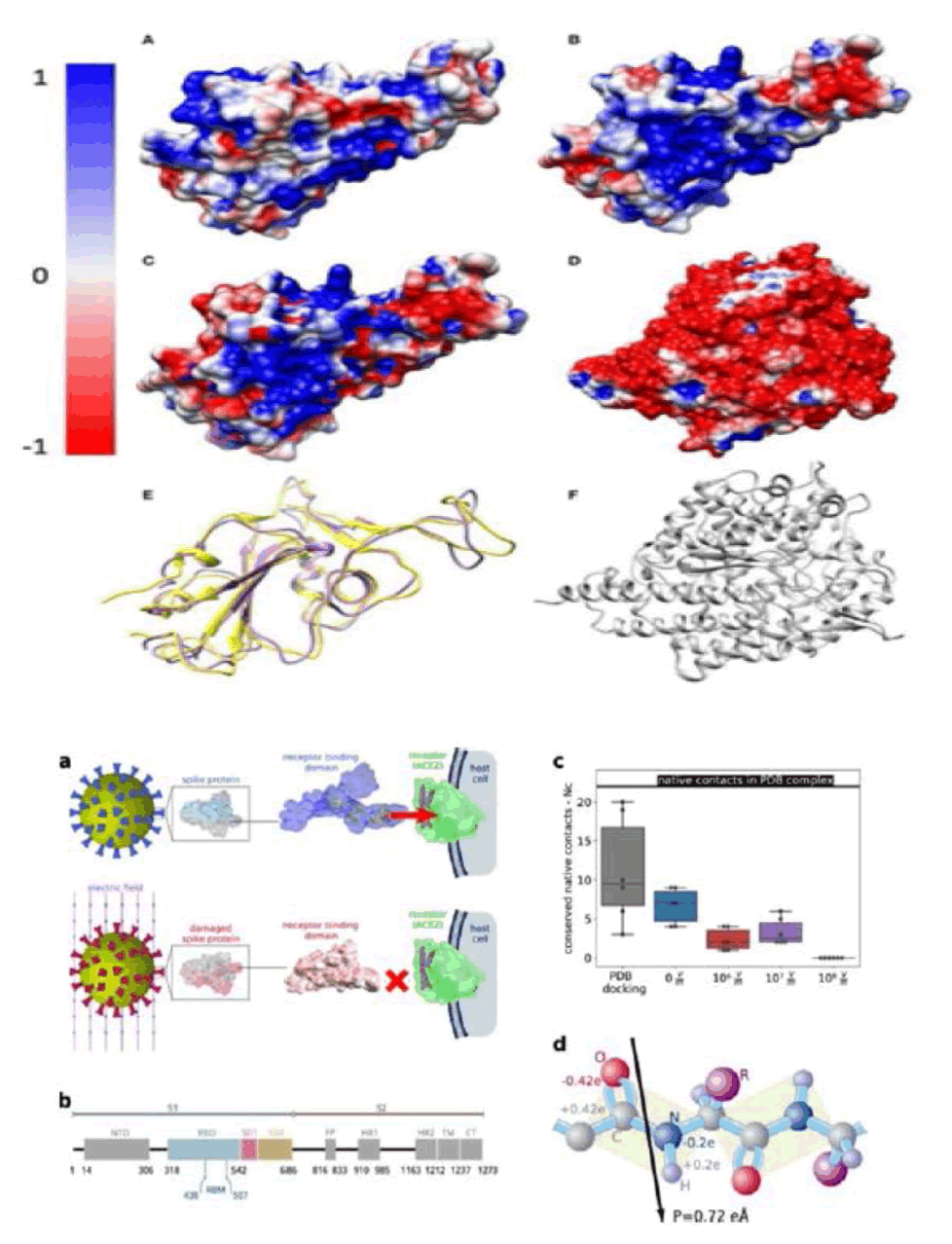
Figure 22: The binding between the S protein and ACE2 can be altered when external electric fields induce drastic conformational changes and damage in the Spike protein. Very strong electric fields (109â??V/m) disable the protein by largely deforming its shape, leaving a structure which is unrecognised by ACE2 (NCâ??=â??0).
Moderate electric fields, which can be induced by available industrial or laboratory devices, strongly reduce NC and are therefore candidates to decrease the affinity of Spike to ACE2 and, consequently, the infectivity of the virus. Electric fields are able to induce global conformational changes in the spike glycoprotein, affecting the stability of folding states. While the structural flexibility of S allows the virus to improve its probability of entering the cell, it is also the origin of the surprising vulnerability of S upon application of electric fields of strengths at least 2 orders of mag nitude smaller than those required for damaging most proteins . The secondary structure of the RBM can be irreversibly perturbed by the electric fields EF , affecting residues that participate in the binding to ACE2. The recognition loop L3 (Tyr470 to Pro491), exhibits 2 parallel β sheets, which are responsible for a higher affinity to ACE215, 42. The electric field induces a change of the secondary structure of L3 to an un-structured loop (example for EF = 107 V m−1) (Figure 23) [22].
Figure 23: Field-induced conformational states can be characterised by the angles formed by the vectors connecting the centroids of clustered residues.
Biotechnology to Combat C.O.V.I.D.-19the Link between Electrical Properties of C.O.V.I.D.-19 and Electromagnetic Radiation Awaad K. Al Sarkhi “Step III Electrical events link with an emitted electromagnetic radiation: In the biological cell, contains ions (the potassium K+ and chloride anion Cl–) are inside the cell, and ions ( Na+, Ca2+ cations, and chloride anion Cl– (at higher concentration) are outside the cell . After the virus enters a host cell leads it to changes the electrical steady state of the virus because the different distribution of electrical charges EC inside and outside the virus leads to an electrical gradient (voltage) across membrane.
This electrical gradient is a difference across viral membrane that generates a store of potential energy in the form of an electro-chemical EC gradient , which helps create the electric field or an electrical potential by the movement of ions across the 2 sides of the membrane. The viral membrane marks the border between the internal and external of the C.O.V.I.D.-19 particle, which means, here the difference in electric potential between the inside and outside the C.O.V.I.D.-19 particle the viral membrane is responsible for the establishment of the electrical potential EP and serves as an insulator, all this indicates that there are lost or gained an electron, so there are lost or gained electrical charges [19].
Case Reports J Neuroradiol. 2022 Reversible neurological and brain MRI changes following C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination: A case report Anuj Rastogi et al “Various neurological sequalae have been described following C.O.V.I.D.19 vaccination. Here we describe the first case of untreated post C.O.V.I.D.19 vaccine encephalitis with spontaneous resolution of contrast enhancing hyperintensities on MRI concomitant with clinical improvement. A 59-yearold woman presented with a 2 day history of unsteady gait, incoordination, visual symptoms, and lethargy. She had received AZD1222 (AstraZeneca AZ ) and mR.N.A.-1273 (Moderna) C.O.V.I.D.-19 vac. at 3 months and 12 days, respectively, before presentation. Brain MRI showed no abnormality on the non-enhanced sequences, but numerous enhancing lesions in the cerebral cortex CC , deep grey matter, brainstem, and in the cerebellum. Treatment was expectant, the patient improved clinically over 10 days, and repeat MRI showed near complete resolution of imaging abnormality.
We describe neurological deterioration 12 days after a second dose of C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine. There was no evidence of edema or demyelinating lesions in brain on M.R.I, but there was extensive contrast-enhancement indicating loss of BB blood-brain barrier integrity. This provides a potential in vivo, clinical-imaging correlate of the post-mortem evidence that S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 spike protein may induce loss of the BBB permeability. While this adds to the list of rare adverse neurological reactions to C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination, the benefits of receiving the vaccine far outweigh these risks [20].
JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Oct Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Midterm Follow Up of C.O.V.I.D.-19 Vaccine–Associated Myocarditis João L. Cavalcante et al “Myocarditis is a rare complication of C.O.V.I.D.-19 mR.N.A. vaccines.1 Although the short-term prognosis is usually favorable, little is known about the longitudinal follow-up and/or midterm prognosis of patients with C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine–associated myocarditis. In nonvaccine-related myocarditis, the persistency of nonischemic myocardial injury on cardiac magnetic resonance CMR imaging is associated with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events.But it is unknown whether the same occurs in COV19VAM. We present CMR imaging findings, as well as clinical characteristics , of 5 adult patients previously affected by COV19VAM . This is the first systematic longitudinal evaluation of both clinical and imaging data up to 3-month follow-up (median follow-up time from first CMR in this study was 106 days; IQR: 75.5-107.5 days) for patients with previous COV19VAM (Figure 24) [21].
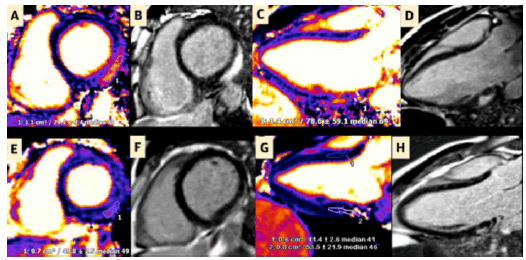
Figure 24: Initial and Follow-Up CMR of Patient 3
(A to D) Initial CMR of patient 3 demonstrating (A and C) prominent myocardial edema and (B and D) LGE of the basal inferior and inferolateral walls consistent with acute myocarditis. (E to H) Follow-up C.M.R demonstrating (E and G) resolution of myocardial edema and (F and H) decrease in nonischemic LGE, consistent with the transition from injury or inflammation to replacement fibrosis. 1 and 2 = regions of interest. “S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 has been widely spread in the world, causing more than 2 million deaths and seriously threatening the human life. Effective protection measures are important to prevent the infection and spreading of the virus. To explore the effects of graphene on the virus adsorption and its biological properties, the adsorption process of the receptor binding domain of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 on graphene has been investigated by molecular dynamics simulations in this work . The results show that R.B.D. can be quickly adsorbed onto the surface of graphene due to π−π stacking and hydrophobic interactions. Residue PHE486 with benzene ring has stronger adsorption force and the maximum contact area with graphene. Graphene significantly affects secondary structure of R.B.D. area, especially on the three key sites of binding with the human ACE2, GLY476, PHE486 and ASN487. The binding free energy of R.B.D. and graphene shows that the adsorption is irreversible (Figure 25) [22,23].
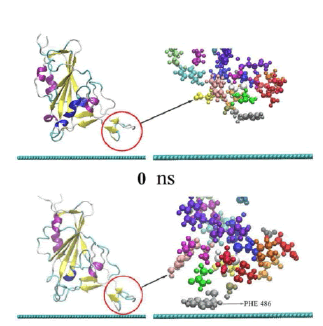
Figure 25: The adsorption process of R.B.D. on the surface of graphene. The left is the secondary structure of R.B.D. presented in newcartoon type, in which the red circle indicates the protein adsorption area. The right is the enlarged CPK type structure of the adsorption area. The blue-green spherical chain below is the side view of 2-dimensional graphene.
Comput Sci Eng. 2020 Nov; 22(6): 21–29. 2020 Aug 11. Revealing the Mechanism of S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding With ACE2 Yixin Xie et al “The S protein R.B.D. is attracted by the A.C.E2 due to their opposite net charges at their binding interfaces. This electrostatic binding force is common in other strong protein–protein interactions, which provides longrange interactions. (Figure 26) [23].
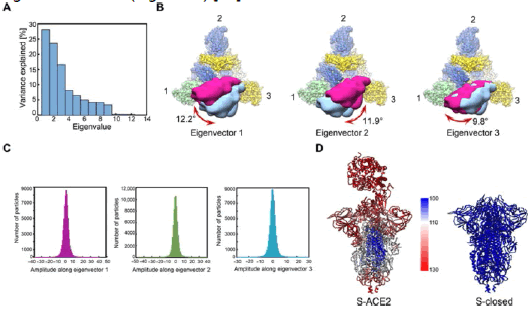
Figure 26: Atomic models of S-ACE2 and S-closed, colored according to the B-factor distribution [ranging from 100 (blue) to 130 Ã?2 (red)]. ACE2 binding to S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 strictly requires the up conformation of R.B.D.
Experimental project hypotesys
In order to verify th effect played by various factor in the relationship between spike protenin ad ACE of pulmonary epitelial cell using an artificial system:
•Cellular colture ( pulmonary epitelial cells) to evaluate the effect of spike protein linked to ACE receptor
•Cellular colture spike -ace plus graphene derivates
•Cellular colture spike-ace- added graphene under electromagnetic field of various intensity and wave( radio or microwave)
•Control group
Result: it is necessary verify if there are not only statistical significance but also clinico-toxicological implication
Time of observation: after 1-2-6-12-24-48-72 hour and more 7 -30- 60 days.
Under an epidemiological point of view It is necessary to consider that young people show no the same level of comorbidity than adults or elderly and that the rare adverse event after some C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination show an class age distribution: rare pericarditys/ myocarditis in young and brain thrombosys under 55 years (24 March 2021 EMA/PRAC/157045/2021 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee). Related proteomics of the link SPIKE protein- ACE2 rec it is of interest to observe that: “R.B.D. can be either in the open or in the closed position (called up or down conformation respectively). In the up conformation, the R.B.D. jut out away from the rest of S, such that they can easily bind with ACE2.
The affinity has increased significantly and/or the elastic energy has been reduced substantially the equilibrium is biased to the open conformation. The open conformational state show more advantageous under an energy point of view “Electric fields are able to induce global conformational changes in the spike glycoprotein. The primary health effect of non-ionizing radiation is temperature production in body tissue [13]. Our results have shown for the first time that the Spike protein has the possibility to stay in an active and inactive state based on the external temperature [14].
Related the pathology presentation :
oth C.O.V.I.D.-19 and W.C.R. exposure can affect the heart and cardiovascular system, directly and/or indirectly [1]. Out of 184 ICU C.O.V.I.D.-19 patients, 31% showed thrombotic complications . Cardiovascular clotting events are a common cause of C.O.V.I.D.-19 deaths . Pulmonary embolism, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC), liver, cardiac, and renal failure have all been observed in C.O.V.I.D.-19 patients [1]. There is a correlation between oxidative stress and thrombogenesis and of interest in animal model: The biological effects on cardiovascular development of chicken embryos were examined after radiation exposure using mobile phone (900 MHz; specific absorption rate˜1.07 W/kg) intermittently 3 h per day during incubation. Samples were selected by morphological and histological methods. The results showed the rate of embryonic mortality and cardiac deformity increased significantly in exposed group (P < 0.05) [4].
Related the graphene chemico –phisical property :
Electrical Property of Graphene and Its Application to Electrochemical Biosensing, Graphene, a single 2-dimensional (2D) layer of a hexagonal structure consisting of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms, and its derivatives have received increasing attention in bio-medical fields, due to its unique physico and chemical properties. This feature includes a high surface area, excellent electrical conductivity, strong mechanical strength, unparalleled thermal conductivity, and ease of surface functionalization. The Spike protein R.B.D. is attracted by the ACE2 due to their opposite net charges at their binding interfaces.
This link increase the epithelial cell penetration . In this work are reported the effect played by electric field on the link between spike protein and the tissue ACE receptor. The same is reported the effect observed in CMR in myocarditys by C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccinated. It is possibe to say that electric – magnetic field can influence the interaction of the spike protein (naturals due by infections) or sintetically by a C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine . But what happen if in this interaction, under electric magnetic umbalance, the graphene molecule and related self assembling propery are present? The electrical properties of graphene are clear by literature. Even if The presence of graphene reduce aggressivity of the coples spike-ACE receptor by an electrical interference there is an increase the duration of the effect. Graphene can assume charge (conductive property) So It is possible to consider the graphene like a carrier that modulate the spike protein toxicicy? Under a toxicological point of view it is always interesting to observe the toxicicty of the various single molecule of factor but especiallly if acting in the same time in a single body. What happen if in the same time after a time related episode the self assembling property of graphene added to spike protein toxicity is influenced by a temporary electromagnetic field? (interference in the system) Two fixed factor plus a variable one: It is possible to divide toxic effect in acute or long term according this situations?
Related this evidence reported and the specific distribution by age of rare pericarditys or CNS thrombosys
After some C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccination Is crucial to more deeply investigate if there are relationship with graphene impurities ( if present) and the wireless radiation or not. The same to verify if this effect can produce pathological event in significative clinical way. Even if the protrombotic and proinflamatory effect of the S.A.R.S. cov-2 spike protein are cleary reported by many scientific database and the effect played by various wireless radiation are studied using various models it is relevant to verify also if a cumulative effect can act on a ptahological common event. The same it is crucial verify if Garphene presence with its electrical conductivity can increase the effect played by electromagnetic field on SPIKE proteinace2 rec. (various independent researcher reported evidence or in vials of vaccine or in blood of vaccinated).
Even if in the various countries C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine Spike protein based have been approved by regulatory agency The report of some rare adverse event in subpopulation or limitation of other vaccine according the age class require a more deeply investigation to find if present relationship of interest (Every year various approved drugs are recalled by authorities due by safety motivations) because toxicity of S.A.R.S. cov-2 virus spike protein can produce clots, pericarditys or other pathologic event . It is of interest to evaluate some additional co- factor in the case of C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine spike based. What happen in presence of graphene derivates and what happen under determinate condition of external electro-magnetic filed and what effect is played by various electromagnetic field intensity applied or by the time of application?
Related this topic it is interesting to observe that there are no or few literature about the effepct played by the combination of spike protein – ace and graphene under various grade of electro- magnetic field. “It has been theoretically predicted and experimentally demonstrated that static and time-dependent electric fields (EFs) are capable of inducing conformational changes or even irreversible damage in proteins” and “ACE2 binding to S.A.R.S.-CoV-2 strictly requires the up conformation of R.B.D.” “Electric fields are able to induce global conformational changes in the spike glycoprotein, affecting the stability of folding states”. (As written by Claudia R. Arbeitman et al) So The intensity and duration of the link between SPIKE and ACE is influenced by electric fields ( maximum or minimum effect according the intensity of interference ).
The rare effect observed for some mR.N.A. Vaccine like pericarditis in young are currently reported in scientific database, the same the procoagulant effect but because there is a variability in this effect it can be relevant observe the environment around the patient body and the real composition of the vaccine vials.
Various independent reseacher finded graphene derivates in some vials of C.O.V.I.D.-19 vaccine and the same other reported this substantie in blood of vaccinated because electro-magentic field can modify the electrical charge of various molecule it is crucial for the author of this work to invesigate deeply the cumulative affect played by this three independent factor (primary or secondary) in the development of adverse event.
Mainly related the intensity of this relationship and during a wide windows of time. Even if the aggressivity of phenomena is not really high the persistence during time can produce pathological effect.
[Google Scholar] [Cross ref]
[Google Scholar] [Cross ref]
[Google Scholar] [Cross ref]
Citation: Gomez, S. et al. S.A.R.S. COV-2 Spike Protein Derivates ACE LINK - Graphene and Wireless Comunications Radiation : Epidemiological Chemico Physical and Toxicological Aspects -Scientific Evidence and Other Interesting Documents 2023, 8(03), 001-013
Received: 12-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. mrcs-23-95113; Editor assigned: 13-Apr-2023, Pre QC No. mrcs-23-95113 (PQ); Reviewed: 20-Apr-2023, QC No. mrcs-23-95113 (Q); Revised: 23-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. mrcs-2395113 (R); Published: 26-Apr-2023, DOI: 10.4172/2572 5130.23.8(03).1000243
Copyright: ©2023 Gomez, S. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.