Research Article - (2022) Volume 13, Issue 2
Introduction: This is the first prospective study that evaluates the functional outcome after a surgical procedure secondary to a traumatic brain injury, in a single centre, in the Dominican Republic.
Objective: To determine the functional status of surgically treated patients 6 months after trauma and to establish the association of functional status with the predictive variables of the International Mission for Prognosis and Analysis of Critical Trials in TBI (IMPACT), determining the relative risk of worse prognosis according to those variables.
Material and method: A prospective, longitudinal study was conducted in a cohort of 22 patients who were surgically treated for a traumatic intracranial injury at Dr Ney Arias Lora Hospital in the Dominican Republic. We applied the IMPACT calculator, (pupillary response, Hg, hypoxia, age, motor response, CT lesion, hypotension, etc.) previous to surgery and the Extended Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS-E) 6 months after surgery to determine the functional outcome. Our team modified the IMPACT form by adding The Glasgow level, pre-surgical time and rehabilitation therapy. The SPSS database (15.0 version, Chicago Il.) was used. Central tendency measures and Fisher's test were applied. A p ≤ 0.05 with a 95% confidence interval was considered statistically significant. Results: The only predictive variable associated with a poor prognosis was the motor response (p=0.01), hypoxia and hypotension (p=0.05). Patients who had any alterations in Motor response had a worse prognosis and higher mortality in this subgroup (RR: 10, 95% CI: 3-22). Normal flexion was found in all patients with good high recovery (p= 0.04).
Conclusion: 67% of patients had a favourable outcome (moderate disability and good recovery). Mortality was 23%. Motor response and Hypoxia, previous to surgery, were powerful outcome prognostic factors.
Blood transfusion • Transfusion transmitted infection • Blood donors
Adjuvant therapy in current neurosurgery has turned the management patterns of various pathologies, allowing better outcomes. Developing technologies such as robotic surgery, dendritic cell vaccines for certain brain tumours, gene therapy, and radiosurgery are some of these promising evolving techniques. Despite this, surgical brain-spine trauma still depends entirely on the surgeon's technical skills. According to World Health Organization, there is 1.35 million death each year due to road traffic injuries. Bruns and Heuser [1] define traumatic brain injury as a critical socio-economic and public health problem, being the leading cause of mortality and disability in young patients. In 2018 there was a total of 2168 death due to traffic accidents in the Dominican Republic, equivalent to a rate of 21 cases per 100,000 habitants, a big increase compared to previous years. This data corroborates with Langlolis [2] and collaborators, who say that each year the number of disabled and killed people by motor vehicle accidents will increase, and trauma will surpass their congeners (cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease) as the number one cause of death worldwide.
This is a prospective, observational pilot study conducted in a cohort of 22 patients who were surgically treated for a traumatic intracranial injury at Dr Ney Arias Lora Hospital in the Dominican Republic between January 1st and July 30th 2018. We applied the IMPACT calculator, (pupillary response, Hg, hypoxia, age, motor response, CT lesion, hypotension, etc.) previous to surgery and the Extended Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS-E) 6 months after surgery to determine the functional outcome. Our team modified the IMPACT form by adding The Glasgow level, pre-surgical time and rehabilitation therapy (Figure 1).
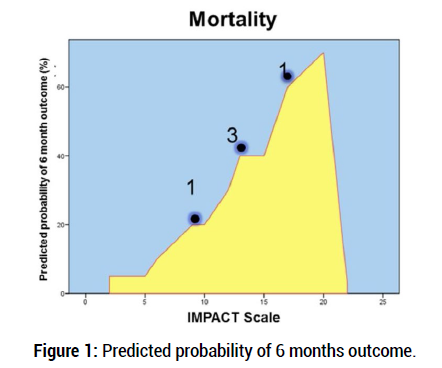
Figure 1: Predicted probability of 6 months outcome.
Patients over the age of 14 years old who were surgically treated for a TBI were included. Cases with incomplete medical records were excluded. Those with multiple surgeries due to polytrauma, during their hospital stay, and those that could not be contacted by phone were excluded as well.
The original primary outcome was to determine the functional status of these surgically treated patients 6 months after trauma (a composite of death, vegetative state, or severe disability) as evaluated on the Extended Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS-E) and to establish the association of functional status with the predictive variables of the International Mission for Prognosis and Analysis of Critical Trials in TBI (IMPACT). Second, to determine the relative risk of a worse prognosis according to those variables.
All patients were males, 63% of them (14 cases) were under 30 years old. The level of consciousness according to the Glasgow scale was heterogeneous, with a slight predominance of severe trauma (GCS < 8/15), within which were most of the deceased. 58% (13) were above 9/15 (Figure 2).
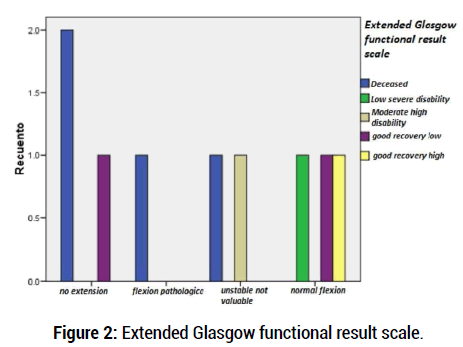
Figure 2: Extended Glasgow functional result scale.
For a better understanding, outcome scores were dichotomized as the favourable outcome (Good recovery/moderate disability) or unfavourable outcome (dead/vegetative/severe disability). 67% of cases had a favourable outcome. 23% (5) of patients died, 3 of them in the acute/subacute hospital setting. We found no association between age and pupillary reactivity compared to functional prognosis, unlike the relationship between hypoxia and survival, as 80% of the deceased patients were in the group with hypoxia data (p=0.009), and all patients with good functional outcomes were not associated with this variable (Table 1 and Table 2).
| Variable | Favorable Outcome (Good recovery moderate disability) |
Unfavorable Outcome (dead/vegetative/severe disability) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glasgow | >8/15 | â?¤8/15 | 0.07 |
| motor response (normal flexion versus abnormal flexion) | Normal flexion | Abnormal flexion or extension | 0.05 |
| hipoxia | No hipoxia | hipoxia | 0.05 |
| Hipotension | No hipotension | hipotension | 0.05 |
Table 1: Outcome related variables.
| Variable | Alive | Death | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| motor response | 2 patients | 4 Patients | 0.01 |
| hipoxia | 2 Patients | 4 Patients | 0.009 |
Table 2: Survival associated variables.
Normal motor response (obey the verbal command, localize to stimuli, normal flexion to stimuli) was associated with a favourable outcome p=0.05. When dichotomized to alive or dead, the motor response is statistically significant p=0.01. Normal flexion was found in all patients with good high recovery. Hypotension and Glasgow Scale at admission were not associated with the outcome in our study.
Optimizing procedures and protocols, in the interest of saving lives and ensuring a better functional result, is vital in medicine, so the search for predictive variables has been, and will remain the north in modern neurosurgery, not only in the context of trauma but all neuropathological entities. Marmorou [3] and collaborators found that pupil response was strongly associated with a worse prognosis, unlike our data, where we found no relationship (p=0.2).
Age, along with the reactivity pupillary have been highlighted as important variables that are predictive, in traumatic brain injury. Choi, et al. [4-5] in a population of 523 patients found that cutting at 50 years of age, threw significant differences; patients with ages above this threshold had a higher probability of a worse prognosis. These data are similar to those of Dominguez and Hodelin [6], who in 2011 conducted research in Cuba with 110 patients, where they found that patients over 60 years of age had a worse outcome. In our study, age did not influence the functional outcome (p=0.2), this is because the majority of the patients (20) were younger than 50 years old and the distribution in relation to the severity of the trauma was homogeneous.
Our results showed a significant association between hypoxia and unfavourable outcome (p=0.009). Baldwin [7-8], and cols, based on income information, analyzed 828 patients from the Traumatic Coma Data Bank (TCDB) by selecting a combination of variables to predict early survival mortality. The elderly, low GCS scores and the presence of pupil alteration, hypotension and hypoxia were associated with mortality. The probability of death was calculated for each subject so that if it was greater than 0.5, mortality was predicted. Predictions were correct in 91.2% of patients. Menon and Zahed [9-10] also noted that hypoxia was associated with unfavourable evolution and poor functional outcome.
The most important database at the global level in relation to prognostic factors and functional outcome is the IMPACT database, it contains a total of 9205 patients with severe /moderate traumatic brain injury, treated in the last 20 years in 8 clinical trials and 3 observational studies. Marmarou, Lu and Butcher [4] examined this database and found a strong association between the motor response and functional outcome 6 months after the trauma (OR 1.74-7.48), the lower the score on motor response, the worse the prognosis of the patient (p=0.0001), these data are consistent with our findings, we show that patients who had a lower score in motor function had an unfavourable outcome compared with those who presented a normal flexion (RR: 3.2 95% CI: 1.2-5.5). All patients with good high and low recovery had normal flexion (p=0.04) should be performed.
The secondary injury should be avoided in surgical TBI patients, factors such as hypoxia and hypotension are the most important modifiable variables in this setting. Although hypotension was not associated with outcome in our research, another prospective statistically powerful study has shown its importance in functional results after TBI.
The motor response is still the most important non-modifiable factor related to outcome (p=0.01). Our study shows similarities between surgical and non-surgical (contrasted with non-surgical studies) TBI patients when we compare prognostic factors previous to surgery.
A small number of subjects were studied (Pilot Study). More powerful prospective studies among surgical TBI patients, and comparing these with non/surgical patients.
CrossRef Google Scholar
CrossRef Google Scholar
CrossRef Google Scholar
CrossRef Google Scholar
CrossRef Google Scholar
Citation: Manuel E, et al. Functional Outcome at 6 Months of Surgical Traumatic Brain Injury: A single Caribbean Center Pilot Study. J Neurol Neurophy, 2022, 13 (2), 001-002.
Received: 22-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. Jnn-22-55160; Editor assigned: 13-Feb-2022, Pre QC No. Jnn-22-55160(PQ); Reviewed: 20-Feb-2022, QC No. heor-22-55160(Q); Revised: 23-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. Jnn-22-55160(R); Published: 28-Feb-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2155-9562.2022.13(2).570
Copyright: © 2022 Manuel E. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.